List of elements
»
Actinium
»
Aluminum
»
Antimony
»
Argon
»
Arsenic
»
astatine
»
Barium
»
Bismuth
»
bohrium
»
Boron
»
Bromine
»
Cadmium
»
Calcium
»
Carbon
»
Cerium
»
cesium
»
Chlorine
»
Chromium
»
Cobalt
»
Copper
»
Curium
»
dubnium
»
Erbium
»
Europium
»
fermium
»
Fluorine
»
francium
»
Gallium
»
Gold
»
Hafnium
»
hassium
»
Helium
»
holmium
»
Hydrogen
»
Indium
»
Iodine
»
Iridium
»
Iron
»
Krypton
»
Lead
»
Lithium
»
lutetium
»
Mercury
»
Neon
»
Nickel
»
Nihonium
»
Niobium
»
Nitrogen
»
nobelium
»
Osmium
»
Oxygen
»
Platinum
»
Polonium
»
Radium
»
Radon
»
Rhenium
»
rhodium
»
Rubidium
»
Samarium
»
scandium
»
Selenium
»
Silicon
»
Silver
»
Sodium
»
Sulfur
»
Tantalum
»
Terbium
»
Thallium
»
Thorium
»
Thulium
»
Tin
»
Titanium
»
Tungsten
»
Uranium
»
Vanadium
»
Xenon
»
Yttrium
»
Zinc
Na - Sodium - ALKALI METAL
Sodium is a chemical element of the alkali metal family that bears the chemical symbol Na. It is the most abundant fundamental element in the oceans and is one of the most abundant elements on Earth.
Pure sodium is a soft, silvery-white metal. It was discovered by Sir Humphrey Davy in 1807. It is very reactive, and reacts very easily with water to form hydrogen and sodium hydroxide.
sodium is widely used in the food industry, being used to salt food. It is also widely used in the chemical industry and to make salt products. sodium is also used in the aluminum industry to produce aluminum.
The main characteristics of sodium are its low density and its low thermal and electrical conductivity. This means that it is an excellent thermal and electrical insulator. It also has a low vapor pressure and is very soluble in water.
The chemical properties of sodium are mainly due to its high reactivity. sodium is very reactive with water, oxygen, sulfuric acid and other substances. The reaction products with oxygen are oxides, while those with water are hydroxides and carbonates.
sodium is used in many industrial applications because it is very reactive and abundant. Some of the common uses include making salts and using as a catalyst in certain chemical reactions. It is also used in the food industry to preserve food and improve its taste. It is also used for the production of aluminum and for the treatment of waste water.
Pure sodium is a soft, silvery-white metal. It was discovered by Sir Humphrey Davy in 1807. It is very reactive, and reacts very easily with water to form hydrogen and sodium hydroxide.
sodium is widely used in the food industry, being used to salt food. It is also widely used in the chemical industry and to make salt products. sodium is also used in the aluminum industry to produce aluminum.
The main characteristics of sodium are its low density and its low thermal and electrical conductivity. This means that it is an excellent thermal and electrical insulator. It also has a low vapor pressure and is very soluble in water.
The chemical properties of sodium are mainly due to its high reactivity. sodium is very reactive with water, oxygen, sulfuric acid and other substances. The reaction products with oxygen are oxides, while those with water are hydroxides and carbonates.
sodium is used in many industrial applications because it is very reactive and abundant. Some of the common uses include making salts and using as a catalyst in certain chemical reactions. It is also used in the food industry to preserve food and improve its taste. It is also used for the production of aluminum and for the treatment of waste water.
Synthetic
Radioactive
Liquid
Gaseous
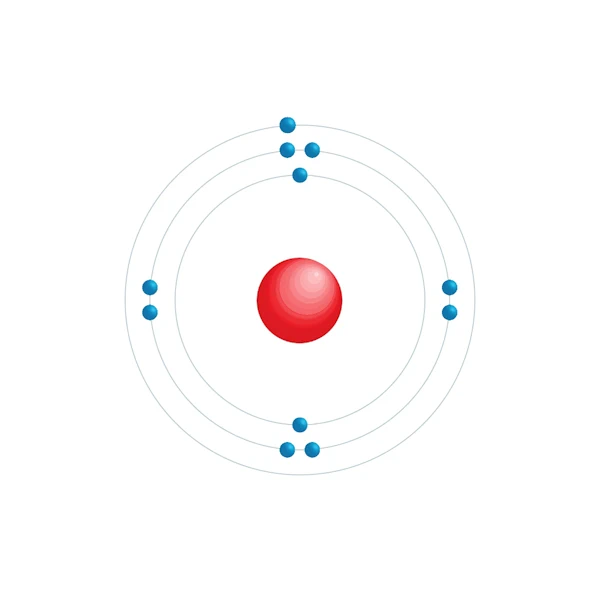
Electronic configuration diagram
| Name | Sodium |
| Number | 11 |
| Atomic | 22.98976928 |
| Symbol | Na |
| Fusion | 97.8 |
| Boiling | 892 |
| Density | 0.971 |
| Period | 3 |
| Group | 1 |
| Discovery | 1807 Davy |
| Abundance | 23600 |
| Radius | 2.2 |
| Electronegativity | 0.93 |
| Ionization | 5.1391 |
| Number of isotopes | 7 |
| Electronic configuration | [Ne] 3s1 |
| Oxidation states | -1,1 |
| Electron by energy level | 2,8,1 |
| Mineral | Hardness | Density |
| Abenakiite-(Ce) | 4.00 / 4.00 | 3.21 |
| Acmonidesite | ||
| Actinolite | 5.50 / 5.50 | 2.98 |
| Adamsite-(Y) | 3.00 / 3.00 | |
| Adranosite | ||
| Adranosite-(Fe) | 2.20 | |
| Aegirine | 6.00 / 6.50 | 3.50 |
| Aegirine-augite | 6.00 / 6.00 | 3.40 |
| Aenigmatite | 5.00 / 6.00 | 3.74 |
| Aerinite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 2.48 |
| Afghanite | 5.50 / 6.00 | 2.55 |
| Agrellite | 5.50 / 5.50 | 2.88 |
| Aiolosite | 3.59 | |
| Ajoite | 2.96 | |
| Albite | 7.00 / 7.00 | 2.61 |
| Alexkhomyakovite | ||
| Alflarsenite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 2.61 |
| Aliettite | 1.00 / 2.00 | |
| Alloriite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.35 |
| Alluaivite | 5.00 / 6.00 | 2.76 |
| Alluaudite | 5.00 / 5.50 | 3.45 |
| Almarudite | 6.00 / 6.00 | 2.71 |
| Alnaperbøeite-(Ce) | ||
| Alsakharovite-Zn | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.90 |
| Altisite | 6.00 / 6.00 | 2.64 |
| Alum-(Na) | 3.00 / 3.00 | 1.67 |
| Alumino-ferrobarroisite | ||
| Alumino-ferrowinchite | ||
| Alumino-magnesiotaramite | ||
| Alumino-ottoliniite | ||
| Aluminobarroisite | 5.00 / 6.00 | 2.94 |
| Aluminokatophorite | 5.00 / 6.00 | |
| Aluminowinchite | ||
| Alumoåkermanite | 4.00 / 5.00 | 3.00 |
| Amarillite | 2.50 / 3.00 | 2.19 |
| Amblygonite | 5.50 / 6.00 | 2.98 |
| Ameghinite | 2.00 / 3.00 | 2.02 |
| Amicite | 5.00 / 5.50 | 2.06 |
| Analcime | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.30 |
| Andersonite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 2.79 |
| Andesine | 7.00 / 7.00 | 2.66 |
| Andrianovite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 3.02 |
| Angarfite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 2.77 |
| Anorthite | 6.00 / 6.00 | 2.72 |
| Anorthoclase | 6.00 / 6.00 | 2.57 |
| Antipinite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 2.55 |
| Apexite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 1.74 |
| Aphthitalite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 2.70 |
| Aqualite | 4.00 / 5.00 | 2.66 |
| Arapovite | 5.50 / 6.00 | 3.43 |
| Arctite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 3.11 |
| Ardennite-(V) | 6.00 / 7.00 | 3.55 |
| Arfvedsonite | 5.50 / 6.00 | 3.44 |
| Arisite-(Ce) | ||
| Arisite-(La) | 3.00 / 3.50 | 4.07 |
| Aristarainite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 2.03 |
| Armbrusterite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 2.78 |
| Arnhemite | 2.33 | |
| Arrojadite-(BaFe) | 3.54 | |
| Arrojadite-(BaNa) | ||
| Arrojadite-(KFe) | 5.00 / 5.00 | 3.50 |
| Arrojadite-(KNa) | ||
| Arrojadite-(NaFe) | ||
| Arrojadite-(PbFe) | 4.00 / 5.00 | |
| Arrojadite-(SrFe) | ||
| Arseniopleite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 4.22 |
| Arsmirandite | ||
| Ashcroftine-(Y) | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.61 |
| Aspidolite | 2.00 / 3.00 | 2.89 |
| Astrophyllite | 3.00 / 3.50 | 3.30 |
| Augite | 5.00 / 6.50 | 3.20 |
| Bakhchisaraitsevite | 2.00 / 2.50 | 2.50 |
| Balliranoite | ||
| Banalsite | 6.00 / 6.00 | 3.07 |
| Bannermanite | 3.50 | |
| Bannisterite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 2.83 |
| Barahonaite-(Al) | ||
| Barahonaite-(Fe) | 3.03 | |
| Barentsite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 2.56 |
| Bario-olgite | 4.00 / 4.50 | 4.00 |
| Barnesite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 3.15 |
| Barrerite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 2.13 |
| Barroisite | 5.00 / 6.00 | 3.00 |
| Barrydawsonite-(Y) | ||
| Barytolamprophyllite | 2.00 / 3.00 | 3.62 |
| Batiferrite | 6.00 / 6.00 | |
| Batisite | 5.90 / 5.90 | 3.43 |
| Bazzite | 6.50 / 6.50 | 2.80 |
| Bederite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 3.48 |
| Beidellite | 1.00 / 2.00 | 2.00 |
| Belakovskiite | ||
| Bellbergite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.20 |
| Belovite-(Ce) | 5.00 / 5.00 | 4.19 |
| Belovite-(La) | 5.00 / 5.00 | 4.19 |
| Benyacarite | 2.50 / 3.00 | 2.40 |
| Beryllonite | 5.50 / 6.00 | 2.80 |
| Berzeliite | 4.50 / 5.00 | 4.08 |
| Betalomonosovite | ||
| Betpakdalite-NaCa | 2.89 |
 mineraly.fr
mineraly.fr
 mineraly.co.uk
mineraly.co.uk
 mineraly.com.de
mineraly.com.de
 mineraly.it
mineraly.it
 mineraly.es
mineraly.es
 mineraly.nl
mineraly.nl
 mineraly.pt
mineraly.pt
 mineraly.se
mineraly.se