List of elements
»
Actinium
»
Aluminum
»
Antimony
»
Argon
»
Arsenic
»
astatine
»
Barium
»
Bismuth
»
bohrium
»
Boron
»
Bromine
»
Cadmium
»
Calcium
»
Carbon
»
Cerium
»
cesium
»
Chlorine
»
Chromium
»
Cobalt
»
Copper
»
Curium
»
dubnium
»
Erbium
»
Europium
»
fermium
»
Fluorine
»
francium
»
Gallium
»
Gold
»
Hafnium
»
hassium
»
Helium
»
holmium
»
Hydrogen
»
Indium
»
Iodine
»
Iridium
»
Iron
»
Krypton
»
Lead
»
Lithium
»
lutetium
»
Mercury
»
Neon
»
Nickel
»
Nihonium
»
Niobium
»
Nitrogen
»
nobelium
»
Osmium
»
Oxygen
»
Platinum
»
Polonium
»
Radium
»
Radon
»
Rhenium
»
rhodium
»
Rubidium
»
Samarium
»
scandium
»
Selenium
»
Silicon
»
Silver
»
Sodium
»
Sulfur
»
Tantalum
»
Terbium
»
Thallium
»
Thorium
»
Thulium
»
Tin
»
Titanium
»
Tungsten
»
Uranium
»
Vanadium
»
Xenon
»
Yttrium
»
Zinc
I - Iodine - NON-METAL HALOGEN
Iodine is a metalloid chemical element belonging to the halogen family and occurring in solid form of an intense violet.
- iodine is an extremely reactive halogen. It combines with many other chemical elements and forms volatile molecules.
- It also combines with hydrogen to form a liquid compound at low temperatures called hydriodic acid.
- It is very soluble in water and dissolves to form iodide ions.
- iodine has many uses, including in x-rays, wastewater treatment to remove chlorine and bromides, and the manufacture of chemicals, such as antiseptics, drugs, and dyes.
- It is also used in the treatment of certain forms of cancer and in the production of radiopharmaceuticals for medical diagnostic examinations.
- iodine is also used in the production of radioactive iodine, which is used in applications such as radio-imaging and cancer treatment.
- iodine is an extremely reactive halogen. It combines with many other chemical elements and forms volatile molecules.
- It also combines with hydrogen to form a liquid compound at low temperatures called hydriodic acid.
- It is very soluble in water and dissolves to form iodide ions.
- iodine has many uses, including in x-rays, wastewater treatment to remove chlorine and bromides, and the manufacture of chemicals, such as antiseptics, drugs, and dyes.
- It is also used in the treatment of certain forms of cancer and in the production of radiopharmaceuticals for medical diagnostic examinations.
- iodine is also used in the production of radioactive iodine, which is used in applications such as radio-imaging and cancer treatment.
Synthetic
Radioactive
Liquid
Gaseous
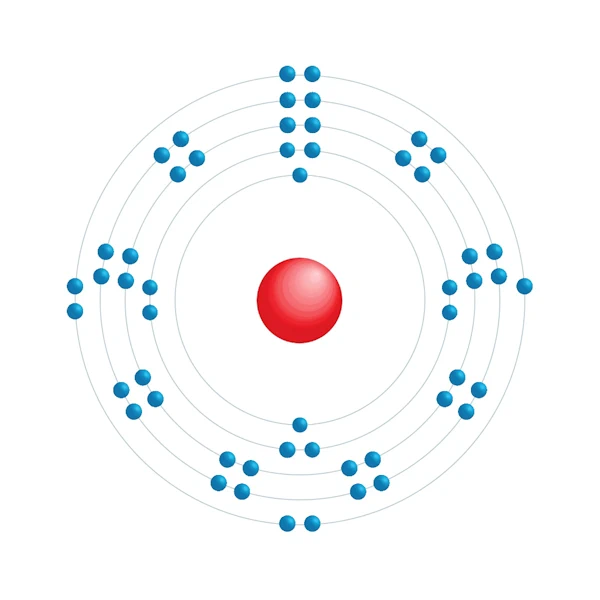
Electronic configuration diagram
| Name | Iodine |
| Number | 53 |
| Atomic | 126.90447 |
| Symbol | I |
| Fusion | 113.5 |
| Boiling | 184.4 |
| Density | 4.93 |
| Period | 5 |
| Group | 17 |
| Discovery | 1811 Courtois |
| Abundance | 0.45 |
| Radius | 1.3 |
| Electronegativity | 2.66 |
| Ionization | 10.4513 |
| Number of isotopes | 24 |
| Electronic configuration | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p5 |
| Oxidation states | -1,1,3,5,7 |
| Electron by energy level | 2,8,18,18,7 |
| Mineral | Hardness | Density |
| Aurivilliusite | 8.96 | |
| Bellingerite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 4.89 |
| Bluebellite | 1.00 / 1.00 | 4.75 |
| Brüggenite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 4.24 |
| Capgaronnite | 6.19 | |
| Carlosruizite | 2.50 / 3.00 | 3.42 |
| Coccinite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 6.00 |
| Demicheleite-(Br) | ||
| Demicheleite-(I) | ||
| Dietzeite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 3.62 |
| Fuenzalidaite | 2.50 / 3.00 | 3.31 |
| George-ericksenite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 3.04 |
| Grechishchevite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 7.16 |
| Hectorfloresite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 2.80 |
| Iodargyrite | 1.50 / 2.00 | 5.50 |
| Iodine | ||
| Lautarite | 3.50 / 4.00 | 4.52 |
| Marshite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 5.60 |
| Miersite | 2.50 / 3.00 | 5.64 |
| Moschelite | 1.50 / 2.00 | 7.00 |
| Mutnovskite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 6.18 |
| Nataliyamalikite | ||
| Perroudite | 2.00 / 2.00 | |
| Radtkeite | 2.00 / 3.00 | 7.00 |
| Salesite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 4.77 |
| Schwartzembergite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 7.39 |
| Seeligerite | 6.83 | |
| Tedhadleyite | 2.50 / 2.50 | |
| Tocornalite | 1.00 / 2.00 | |
| Vasilyevite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 9.57 |
 mineraly.fr
mineraly.fr
 mineraly.co.uk
mineraly.co.uk
 mineraly.com.de
mineraly.com.de
 mineraly.it
mineraly.it
 mineraly.es
mineraly.es
 mineraly.nl
mineraly.nl
 mineraly.pt
mineraly.pt
 mineraly.se
mineraly.se