List of elements
»
Actinium
»
Aluminum
»
Antimony
»
Argon
»
Arsenic
»
astatine
»
Barium
»
Bismuth
»
bohrium
»
Boron
»
Bromine
»
Cadmium
»
Calcium
»
Carbon
»
Cerium
»
cesium
»
Chlorine
»
Chromium
»
Cobalt
»
Copper
»
Curium
»
dubnium
»
Erbium
»
Europium
»
fermium
»
Fluorine
»
francium
»
Gallium
»
Gold
»
Hafnium
»
hassium
»
Helium
»
holmium
»
Hydrogen
»
Indium
»
Iodine
»
Iridium
»
Iron
»
Krypton
»
Lead
»
Lithium
»
lutetium
»
Mercury
»
Neon
»
Nickel
»
Nihonium
»
Niobium
»
Nitrogen
»
nobelium
»
Osmium
»
Oxygen
»
Platinum
»
Polonium
»
Radium
»
Radon
»
Rhenium
»
rhodium
»
Rubidium
»
Samarium
»
scandium
»
Selenium
»
Silicon
»
Silver
»
Sodium
»
Sulfur
»
Tantalum
»
Terbium
»
Thallium
»
Thorium
»
Thulium
»
Tin
»
Titanium
»
Tungsten
»
Uranium
»
Vanadium
»
Xenon
»
Yttrium
»
Zinc
mineralogy
elements
Sb Antimony
Sb - Antimony - METALLOIDS
Antimony is a metallic chemical element, denoted Sb and with atomic number 51, which is part of group 15 of the periodic table of elements. It is a shiny white metal, which turns into a colorless powder when exposed to air.
The physical properties of antimony are: Density: 6.69 g/cm3, melting point: 630°C, boiling point: 1587°C and flash point: 630°C.
antimony has interesting chemical properties such as: it is very reactive with acids, and dissolves easily in acidic solutions; it can react vigorously with halogens; and it reacts with oxygen, halogens and salts to form oxoacidic compounds.
antimony is mainly used to make metal alloys, batteries, semiconductors and catalysts. It is also frequently used in the textile industry, chemical industry and dye industry. antimony compounds are also used as insecticides and fungicides.
The physical properties of antimony are: Density: 6.69 g/cm3, melting point: 630°C, boiling point: 1587°C and flash point: 630°C.
antimony has interesting chemical properties such as: it is very reactive with acids, and dissolves easily in acidic solutions; it can react vigorously with halogens; and it reacts with oxygen, halogens and salts to form oxoacidic compounds.
antimony is mainly used to make metal alloys, batteries, semiconductors and catalysts. It is also frequently used in the textile industry, chemical industry and dye industry. antimony compounds are also used as insecticides and fungicides.
Synthetic
Radioactive
Liquid
Gaseous
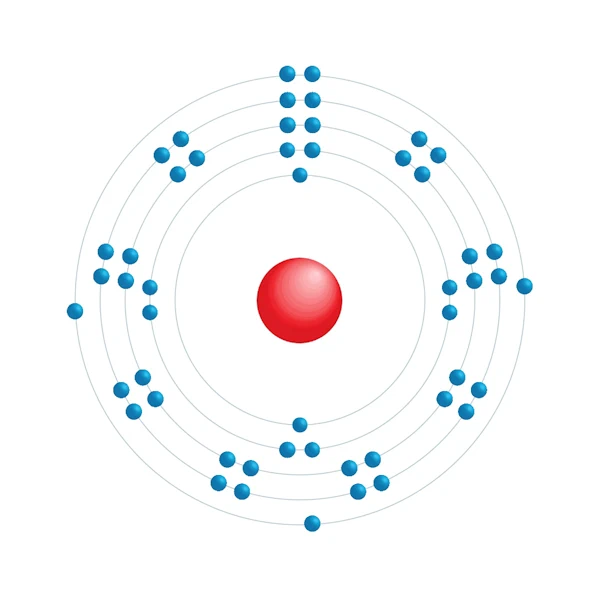
Electronic configuration diagram
| Name | Antimony |
| Number | 51 |
| Atomic | 121.76 |
| Symbol | Sb |
| Fusion | 630.7 |
| Boiling | 1750 |
| Density | 6.685 |
| Period | 5 |
| Group | 15 |
| Discovery | 0 Early historic times |
| Abundance | 0.2 |
| Radius | 1.5 |
| Electronegativity | 2.05 |
| Ionization | 8.6084 |
| Number of isotopes | 29 |
| Electronic configuration | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p3 |
| Oxidation states | -3,3,5 |
| Electron by energy level | 2,8,18,18,5 |
| Mineral | Hardness | Density |
| Allargentum | 4.00 / 4.00 | 10.00 |
| Ambrinoite | 3.31 | |
| Andorite IV | 3.50 / 3.50 | 5.00 |
| Andorite VI | 3.50 / 3.50 | 5.00 |
| Andreadiniite | ||
| Antimonselite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 5.88 |
| Antimony | 3.00 / 3.50 | 6.61 |
| Anyuiite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 13.00 |
| Apuanite | 4.00 / 5.00 | 5.33 |
| Aramayoite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 5.60 |
| Ardaite | 2.50 / 3.00 | 6.00 |
| Argentotennantite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 5.00 |
| Argentotetrahedrite | ||
| Arsenopalladinite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 10.40 |
| Arsenpolybasite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 6.18 |
| Arsenquatrandorite | ||
| Auroantimonate | 4.00 / 4.00 | |
| Aurostibite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 9.98 |
| Bahianite | 9.00 / 9.00 | 4.89 |
| Barikaite | 5.34 | |
| Baumstarkite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 5.33 |
| Benavidesite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 5.60 |
| Benleonardite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 7.00 |
| Bernardite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 4.50 |
| Bernarlottiite | ||
| Berthierite | 2.00 / 2.50 | 4.00 |
| Biehlite | 1.00 / 1.50 | |
| Billwiseite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 6.33 |
| Bindheimite | 4.00 / 5.00 | 4.60 |
| Bismutostibiconite | 4.00 / 5.00 | 7.38 |
| Bitikleite | ||
| Blatterite | 6.00 / 6.00 | 4.70 |
| Borodaevite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 7.90 |
| Borovskite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 8.12 |
| Boscardinite | 3.00 | |
| Bottinoite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 2.83 |
| Boulangerite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 5.70 |
| Bournonite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 5.70 |
| Braithwaiteite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 3.75 |
| Brandholzite | 2.00 / 3.00 | |
| Breithauptite | 3.50 / 4.00 | 8.23 |
| Brizziite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 4.00 |
| Byströmite | 7.00 / 7.00 | 5.70 |
| Camérolaite | 3.10 | |
| Carducciite | 2.50 / 3.00 | 5.56 |
| Cervantite | 4.00 / 5.00 | 6.40 |
| Cesplumtantite | 7.00 / 7.00 | 6.00 |
| Cetineite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 4.00 |
| Chabournéite | 3.00 / 3.50 | 5.10 |
| Chalcostibite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 4.75 |
| Chalcothallite | 2.00 / 2.50 | 6.60 |
| Chapmanite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 3.58 |
| Chestermanite | 6.00 / 6.00 | 3.72 |
| Choloalite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 6.40 |
| Chovanite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 6.03 |
| Ciriottiite | ||
| Clerite | 3.50 / 4.00 | 4.93 |
| Clino-oscarkempffite | ||
| Clinocervantite | ||
| Colusite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 4.20 |
| Coquandite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 5.00 |
| Costibite | 6.00 / 6.00 | 6.89 |
| Criddleite | 3.00 / 3.50 | 6.00 |
| Cualstibite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 3.18 |
| Cuboargyrite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 5.33 |
| Cupropolybasite | 3.00 / 3.50 | 6.31 |
| Cuprostibite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 8.42 |
| Cyanophyllite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 3.10 |
| Cylindrite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 5.40 |
| Dadsonite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 5.68 |
| Dalnegroite | 3.00 / 3.50 | |
| Derbylite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 4.50 |
| Diaphorite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 6.00 |
| Disulfodadsonite | ||
| Dyscrasite | 3.50 / 4.00 | 9.40 |
| Dzhuluite | 4.71 | |
| Ecrinsite | ||
| Falkmanite | 2.00 / 3.00 | 6.31 |
| Famatinite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 4.57 |
| Ferdowsiite | 2.50 / 3.00 | 5.30 |
| Fettelite | 3.50 / 4.00 | 6.29 |
| Filipstadite | 6.00 / 6.50 | 4.00 |
| Fizélyite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 5.56 |
| Florensovite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 4.00 |
| Fluorcalcioroméite | 5.50 / 5.50 | 5.11 |
| Folvikite | ||
| Franckeite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 5.50 |
| Freibergite | 3.50 / 4.00 | 4.85 |
| Freieslebenite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 6.20 |
| Fülöppite | 2.00 / 2.50 | 5.22 |
| Gabrielite | 1.50 / 2.00 | 5.38 |
| Galkhaite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 5.40 |
| Garavellite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 5.64 |
| Genkinite | 5.50 / 6.00 | 8.83 |
| Geocronite | 2.50 / 3.00 | 6.40 |
| Gerstleyite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 3.62 |
| Getchellite | 1.50 / 2.00 | 3.92 |
| Geversite | 4.50 / 5.00 | 10.97 |
| Giessenite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 7.45 |
 mineraly.fr
mineraly.fr
 mineraly.co.uk
mineraly.co.uk
 mineraly.com.de
mineraly.com.de
 mineraly.it
mineraly.it
 mineraly.es
mineraly.es
 mineraly.nl
mineraly.nl
 mineraly.pt
mineraly.pt
 mineraly.se
mineraly.se