List of elements
»
Actinium
»
Aluminum
»
Antimony
»
Argon
»
Arsenic
»
astatine
»
Barium
»
Bismuth
»
bohrium
»
Boron
»
Bromine
»
Cadmium
»
Calcium
»
Carbon
»
Cerium
»
cesium
»
Chlorine
»
Chromium
»
Cobalt
»
Copper
»
Curium
»
dubnium
»
Erbium
»
Europium
»
fermium
»
Fluorine
»
francium
»
Gallium
»
Gold
»
Hafnium
»
hassium
»
Helium
»
holmium
»
Hydrogen
»
Indium
»
Iodine
»
Iridium
»
Iron
»
Krypton
»
Lead
»
Lithium
»
lutetium
»
Mercury
»
Neon
»
Nickel
»
Nihonium
»
Niobium
»
Nitrogen
»
nobelium
»
Osmium
»
Oxygen
»
Platinum
»
Polonium
»
Radium
»
Radon
»
Rhenium
»
rhodium
»
Rubidium
»
Samarium
»
scandium
»
Selenium
»
Silicon
»
Silver
»
Sodium
»
Sulfur
»
Tantalum
»
Terbium
»
Thallium
»
Thorium
»
Thulium
»
Tin
»
Titanium
»
Tungsten
»
Uranium
»
Vanadium
»
Xenon
»
Yttrium
»
Zinc
Cu - Copper - TRANSITION METAL
Copper is a transition metal with the chemical symbol Cu. Its color is orange-red. It has been appreciated for millennia for its unique properties and is the basis of a large number of alloys, including bronze and tin.
copper is one of the most abundant transition metals and is found naturally in several minerals. It is a malleable and ductile metal, which means it can be easily formed and molded into a desired shape. It is lightweight and highly resistant to corrosion and oxidation. The high thermal and electrical conductivity of copper are two of its most important characteristics.
copper is an excellent source of thermal and electrical conductivity and is therefore highly valued for applications where grounding is essential. It is also flammable but only ignites if the temperature is high enough. It is very malleable and has excellent weldability. copper is highly resistant to corrosion and oxidation making it very durable and reliable for long term use.
copper is widely used in industries such as construction, electrical and automation. It is also used in pipes, air conditioning systems, mechanical components and cables. It is popular in jewelry and decorative pieces due to its rich color and ability to form detailed objects. It is also used in the maritime and aeronautical industry.
copper is one of the most abundant transition metals and is found naturally in several minerals. It is a malleable and ductile metal, which means it can be easily formed and molded into a desired shape. It is lightweight and highly resistant to corrosion and oxidation. The high thermal and electrical conductivity of copper are two of its most important characteristics.
copper is an excellent source of thermal and electrical conductivity and is therefore highly valued for applications where grounding is essential. It is also flammable but only ignites if the temperature is high enough. It is very malleable and has excellent weldability. copper is highly resistant to corrosion and oxidation making it very durable and reliable for long term use.
copper is widely used in industries such as construction, electrical and automation. It is also used in pipes, air conditioning systems, mechanical components and cables. It is popular in jewelry and decorative pieces due to its rich color and ability to form detailed objects. It is also used in the maritime and aeronautical industry.
Synthetic
Radioactive
Liquid
Gaseous
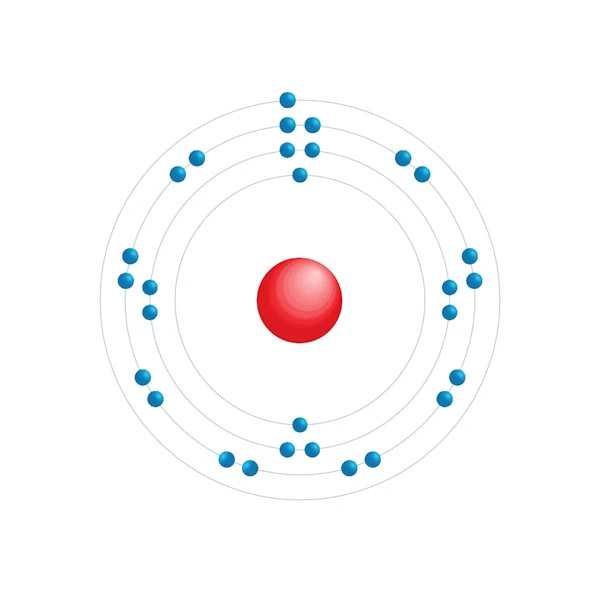
Electronic configuration diagram
| Name | Copper |
| Number | 29 |
| Atomic | 63.546 |
| Symbol | Cu |
| Fusion | 1083.5 |
| Boiling | 2595 |
| Density | 8.96 |
| Period | 4 |
| Group | 11 |
| Discovery | 0 Prehistoric |
| Abundance | 60 |
| Radius | 1.6 |
| Electronegativity | 1.9 |
| Ionization | 7.7264 |
| Number of isotopes | 11 |
| Electronic configuration | [Ar] 3d10 4s1 |
| Oxidation states | 1,2,3,4 |
| Electron by energy level | 2,8,18,1 |
| Mineral | Hardness | Density |
| Abswurmbachite | 6.50 / 6.50 | 4.96 |
| Agaite | 6.99 | |
| Agardite-(Ce) | 3.00 / 3.00 | 3.72 |
| Agardite-(La) | 3.00 / 4.00 | 3.72 |
| Agardite-(Nd) | 3.00 / 4.00 | 3.72 |
| Agardite-(Y) | 3.00 / 4.00 | 3.66 |
| Aikinite | 2.00 / 2.50 | 6.10 |
| Ajoite | 2.96 | |
| Aktashite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 5.50 |
| Aldridgeite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 3.33 |
| Algodonite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 8.38 |
| Allochalcoselite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 4.65 |
| Alpersite | 2.50 / 2.50 | |
| Alumoklyuchevskite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 3.10 |
| Ammineite | ||
| Anatacamite | 4.00 / 4.50 | |
| Andreadiniite | ||
| Andychristyite | 2.00 / 3.00 | 6.30 |
| Andyrobertsite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 4.01 |
| Ángelaite | ||
| Anilite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 5.68 |
| Ankinovichite | 2.50 / 3.00 | 2.48 |
| Annivite | ||
| Anthonyite | 2.00 / 2.00 | |
| Antipinite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 2.55 |
| Antlerite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 3.90 |
| Apachite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 2.80 |
| Arcubisite | ||
| Argentotennantite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 5.00 |
| Arhbarite | ||
| Arsenpolybasite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 6.18 |
| Arsentsumebite | 4.00 / 5.00 | 6.46 |
| Arsmirandite | ||
| Arthurite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 3.02 |
| Arzrunite | ||
| Ashburtonite | 4.69 | |
| Astrocyanite-(Ce) | 2.00 / 3.00 | 3.80 |
| Atacamite | 3.00 / 3.50 | 3.76 |
| Athabascaite | 2.50 / 3.00 | 6.00 |
| Atlasovite | 2.00 / 2.50 | 4.20 |
| Attikaite | 2.00 / 2.50 | 3.20 |
| Aubertite | 2.00 / 3.00 | 1.82 |
| Auriacusite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 4.45 |
| Aurichalcite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 3.64 |
| Auricupride | 2.00 / 3.00 | 11.50 |
| Avdoninite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 3.03 |
| Averievite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 3.54 |
| Azurite | 3.50 / 4.00 | 3.77 |
| Babánekite | ||
| Bairdite | ||
| Balkanite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 6.32 |
| Balyakinite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 5.64 |
| Bambollaite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 5.64 |
| Bandylite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 2.81 |
| Barahonaite-(Al) | ||
| Barahonaite-(Fe) | 3.03 | |
| Barium-zinc alumopharmocosiderite | 2.50 / 2.50 | |
| Barlowite | 2.00 / 2.50 | 4.21 |
| Barquillite | 4.00 / 4.50 | 4.53 |
| Barrotite | ||
| Bayldonite | 4.50 / 4.50 | 5.50 |
| Beaverite-(Cu) | ||
| Bechererite | 2.50 / 3.00 | 3.45 |
| Belendorffite | 2.50 / 4.00 | 13.20 |
| Bellidoite | 1.50 / 2.00 | 7.03 |
| Bellingerite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 4.89 |
| Belloite | 1.00 / 2.00 | 3.79 |
| Benjaminite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 6.70 |
| Benleonardite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 7.00 |
| Berryite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 6.70 |
| Berzelianite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 6.70 |
| Betekhtinite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 5.96 |
| Bezsmertnovite | 4.50 / 4.50 | 16.30 |
| Bilibinskite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 14.27 |
| Birchite | 3.50 / 4.00 | 3.61 |
| Bleasdaleite | 2.00 / 2.00 | |
| Blossite | 3.95 | |
| Bluebellite | 1.00 / 1.00 | 4.75 |
| Bobkingite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 3.25 |
| Bobmeyerite | 4.38 | |
| Bogdanovite | 4.00 / 4.50 | |
| Boleite | 3.00 / 3.50 | 4.80 |
| Bonattite | 2.68 | |
| Boothite | 2.00 / 2.50 | 2.10 |
| Borisenkoite | ||
| Bornite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 4.90 |
| Bortnikovite | 4.50 / 5.00 | 11.16 |
| Botallackite | 3.60 | |
| Bournonite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 5.70 |
| Bradaczekite | ||
| Braithwaiteite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 3.75 |
| Brass | ||
| Briartite | 3.50 / 4.00 | 4.50 |
| Brochantite | 3.50 / 4.00 | 3.97 |
| Brodtkorbite | 2.50 / 3.00 | 7.77 |
| Brumadoite | 1.00 / 1.00 | 4.77 |
| Bukovite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 7.36 |
| Burnsite | 1.00 / 1.50 | |
| Bushmakinite | 3.00 / 3.50 | 6.22 |
 mineraly.fr
mineraly.fr
 mineraly.co.uk
mineraly.co.uk
 mineraly.com.de
mineraly.com.de
 mineraly.it
mineraly.it
 mineraly.es
mineraly.es
 mineraly.nl
mineraly.nl
 mineraly.pt
mineraly.pt
 mineraly.se
mineraly.se