List of elements
»
Actinium
»
Aluminum
»
Antimony
»
Argon
»
Arsenic
»
astatine
»
Barium
»
Bismuth
»
bohrium
»
Boron
»
Bromine
»
Cadmium
»
Calcium
»
Carbon
»
Cerium
»
cesium
»
Chlorine
»
Chromium
»
Cobalt
»
Copper
»
Curium
»
dubnium
»
Erbium
»
Europium
»
fermium
»
Fluorine
»
francium
»
Gallium
»
Gold
»
Hafnium
»
hassium
»
Helium
»
holmium
»
Hydrogen
»
Indium
»
Iodine
»
Iridium
»
Iron
»
Krypton
»
Lead
»
Lithium
»
lutetium
»
Mercury
»
Neon
»
Nickel
»
Nihonium
»
Niobium
»
Nitrogen
»
nobelium
»
Osmium
»
Oxygen
»
Platinum
»
Polonium
»
Radium
»
Radon
»
Rhenium
»
rhodium
»
Rubidium
»
Samarium
»
scandium
»
Selenium
»
Silicon
»
Silver
»
Sodium
»
Sulfur
»
Tantalum
»
Terbium
»
Thallium
»
Thorium
»
Thulium
»
Tin
»
Titanium
»
Tungsten
»
Uranium
»
Vanadium
»
Xenon
»
Yttrium
»
Zinc
mineralogy
elements
Mo Molybdenum
Mo - Molybdenum - TRANSITION METAL
Molybdenum is a chemical element belonging to the group of transition metals. Its chemical symbol is Mo and its atomic number is 42. Its most common oxidation state is +6.
molybdenum is a white-grey metal in its pure state. It is very hard and ductile and has low electrical conductivity. It also has a high resistance to corrosion and heat and can be used at high temperatures (up to 1000°C). molybdenum is the 24th most abundant element in the earth's crust and is present in various minerals.
molybdenum is used in many industrial and commercial applications, including the manufacture of alloys, the production of stainless steels, the production of catalysts and the manufacture of lubricants. It is also used in the nuclear and astronautical industry, due to its high resistance to heat and corrosion. molybdenum is also used in medicine as an isotopic tracer for organ diagnosis and mapping.
molybdenum is a white-grey metal in its pure state. It is very hard and ductile and has low electrical conductivity. It also has a high resistance to corrosion and heat and can be used at high temperatures (up to 1000°C). molybdenum is the 24th most abundant element in the earth's crust and is present in various minerals.
molybdenum is used in many industrial and commercial applications, including the manufacture of alloys, the production of stainless steels, the production of catalysts and the manufacture of lubricants. It is also used in the nuclear and astronautical industry, due to its high resistance to heat and corrosion. molybdenum is also used in medicine as an isotopic tracer for organ diagnosis and mapping.
Synthetic
Radioactive
Liquid
Gaseous
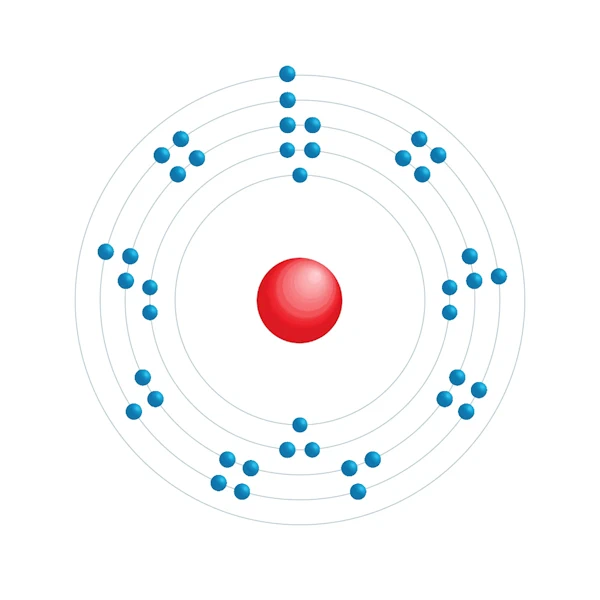
Electronic configuration diagram
| Name | Molybdenum |
| Number | 42 |
| Atomic | 95.95 |
| Symbol | Mo |
| Fusion | 2617 |
| Boiling | 5560 |
| Density | 10.22 |
| Period | 5 |
| Group | 6 |
| Discovery | 1778 Scheele |
| Abundance | 1.2 |
| Radius | 2 |
| Electronegativity | 2.16 |
| Ionization | 7.0924 |
| Number of isotopes | 20 |
| Electronic configuration | [Kr] 4d5 5s1 |
| Oxidation states | -2,-1,1,2,3,4,5,6 |
| Electron by energy level | 2,8,18,13,1 |
| Mineral | Hardness | Density |
| Bamfordite | 2.00 / 3.00 | 3.62 |
| Betpakdalite-CaCa | 3.00 / 3.00 | 2.91 |
| Betpakdalite-CaMg | 3.50 / 3.50 | 2.94 |
| Betpakdalite-NaCa | 2.89 | |
| Betpakdalite-NaNa | 3.00 / 3.00 | 2.88 |
| Biehlite | 1.00 / 1.50 | |
| Calcurmolite | ||
| Chiluite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 3.65 |
| Cousinite | ||
| Cupromolybdite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 4.51 |
| Deloryite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 4.90 |
| Drysdallite | 1.00 / 1.50 | 6.25 |
| Ekplexite | 1.00 / 1.00 | 3.63 |
| Ferrimolybdite | 2.50 / 3.00 | 4.00 |
| Gelosaite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 5.11 |
| Hemusite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 4.47 |
| Hereroite | 8.15 | |
| Hexamolybdenum | 11.90 | |
| Huenite | ||
| Ichnusaite | 4.26 | |
| Ilsemannite | 5.50 / 6.00 | |
| Iriginite | 1.00 / 2.00 | 3.84 |
| Iseite | ||
| Jordisite | 1.00 / 2.00 | |
| Kamiokite | 4.50 / 4.50 | 5.96 |
| Kaskasite | 1.00 / 1.00 | 3.83 |
| Koechlinite | 8.26 | |
| Lindgrenite | 4.50 / 4.50 | 4.26 |
| Maikainite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 4.45 |
| Majindeite | 5.54 | |
| Mambertiite | ||
| Manganokaskasite | 1.00 / 1.00 | 4.09 |
| Markascherite | 3.50 / 4.00 | 4.22 |
| Melkovite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 2.97 |
| Mendozavilite-KCa | 2.50 / 2.50 | |
| Mendozavilite-NaCu | 2.50 / 2.50 | |
| Mendozavilite-NaFe | 1.50 / 1.50 | 2.95 |
| Moluranite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 4.00 |
| Molybdenite | 1.00 / 1.00 | 5.50 |
| Molybdenum | ||
| Molybdite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 4.72 |
| Molybdofornacite | 2.00 / 3.00 | 6.60 |
| Monipite | ||
| Mosesite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 7.72 |
| Mourite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 4.17 |
| Nuragheite | 5.15 | |
| Obradovicite-KCu | 2.50 / 2.50 | 3.68 |
| Obradovicite-NaCu | 2.00 / 2.00 | |
| Obradovicite-NaNa | 2.00 / 2.00 | |
| Ovamboite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 4.74 |
| Paramendozavilite | 1.00 / 1.00 | 3.35 |
| Parkinsonite | 2.00 / 2.50 | 7.32 |
| Powellite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 4.34 |
| Sardignaite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 4.82 |
| Schlegelite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 7.23 |
| Sedovite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 4.20 |
| Sidwillite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 3.12 |
| Suseinargiuite | ||
| Szenicsite | 3.50 / 4.00 | 4.26 |
| Tancaite-(Ce) | ||
| Tarkianite | 5.50 / 6.00 | 7.30 |
| Tengchongite | 2.00 / 2.50 | 4.25 |
| Tugarinovite | 4.60 / 4.60 | 6.00 |
| Umohoite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 4.55 |
| Vajdakite | 3.50 | |
| Vergasovaite | 4.00 / 5.00 | |
| Wulfenite | 2.50 / 3.00 | 6.50 |
 mineraly.fr
mineraly.fr
 mineraly.co.uk
mineraly.co.uk
 mineraly.com.de
mineraly.com.de
 mineraly.it
mineraly.it
 mineraly.es
mineraly.es
 mineraly.nl
mineraly.nl
 mineraly.pt
mineraly.pt
 mineraly.se
mineraly.se