List of elements
»
Actinium
»
Aluminum
»
Antimony
»
Argon
»
Arsenic
»
astatine
»
Barium
»
Bismuth
»
bohrium
»
Boron
»
Bromine
»
Cadmium
»
Calcium
»
Carbon
»
Cerium
»
cesium
»
Chlorine
»
Chromium
»
Cobalt
»
Copper
»
Curium
»
dubnium
»
Erbium
»
Europium
»
fermium
»
Fluorine
»
francium
»
Gallium
»
Gold
»
Hafnium
»
hassium
»
Helium
»
holmium
»
Hydrogen
»
Indium
»
Iodine
»
Iridium
»
Iron
»
Krypton
»
Lead
»
Lithium
»
lutetium
»
Mercury
»
Neon
»
Nickel
»
Nihonium
»
Niobium
»
Nitrogen
»
nobelium
»
Osmium
»
Oxygen
»
Platinum
»
Polonium
»
Radium
»
Radon
»
Rhenium
»
rhodium
»
Rubidium
»
Samarium
»
scandium
»
Selenium
»
Silicon
»
Silver
»
Sodium
»
Sulfur
»
Tantalum
»
Terbium
»
Thallium
»
Thorium
»
Thulium
»
Tin
»
Titanium
»
Tungsten
»
Uranium
»
Vanadium
»
Xenon
»
Yttrium
»
Zinc
mineralogy
elements
Rh rhodium
Rh - rhodium - TRANSITION METAL
Rhodium is a transition metal from the white platinum family, and it is one of the most expensive metals in the world. Its atomic number is 45 and its symbol is Rh.
rhodium is a silvery-white metal that is very refractory and resistant to oxidation. It is one of the hardest and shinier metals, with a specific hardness of 16.3 (compared to 4.5 for gold and 5.5 for platinum).
rhodium is highly wettable and highly refractory, making it the optimal metal for polishing and plating precious metals. It is also insensitive to hydrochloric acid and does not react to weak acids.
rhodium is mainly used in alloys, coatings and in industrial applications. It is also used for plating jewelry and coins. rhodium is also used as a catalyst in hydrogenation processes and is very effective in converting hydrocarbons into more valuable and volatile products. Finally, rhodium is also used as a coating for glasses to increase their resistance to corrosion and heat.
rhodium is a silvery-white metal that is very refractory and resistant to oxidation. It is one of the hardest and shinier metals, with a specific hardness of 16.3 (compared to 4.5 for gold and 5.5 for platinum).
rhodium is highly wettable and highly refractory, making it the optimal metal for polishing and plating precious metals. It is also insensitive to hydrochloric acid and does not react to weak acids.
rhodium is mainly used in alloys, coatings and in industrial applications. It is also used for plating jewelry and coins. rhodium is also used as a catalyst in hydrogenation processes and is very effective in converting hydrocarbons into more valuable and volatile products. Finally, rhodium is also used as a coating for glasses to increase their resistance to corrosion and heat.
Synthetic
Radioactive
Liquid
Gaseous
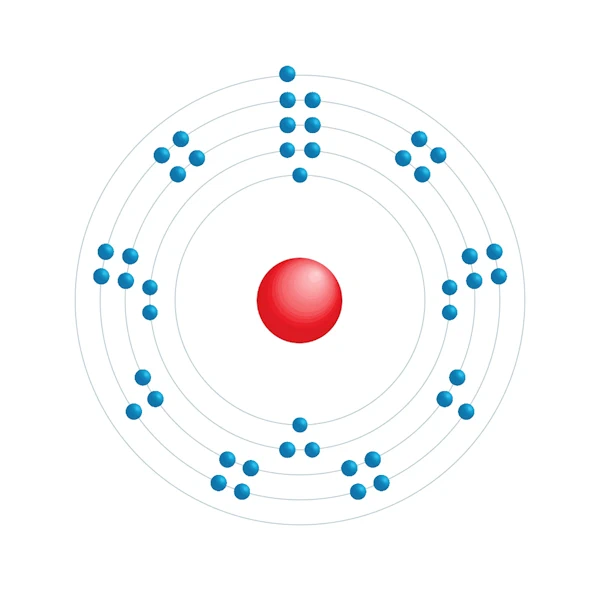
Electronic configuration diagram
| Name | rhodium |
| Number | 45 |
| Atomic | 102.9055 |
| Symbol | Rh |
| Fusion | 1966 |
| Boiling | 3727 |
| Density | 12.41 |
| Period | 5 |
| Group | 9 |
| Discovery | 1803 Wollaston |
| Abundance | 0.001 |
| Radius | 1.8 |
| Electronegativity | 2.28 |
| Ionization | 7.4589 |
| Number of isotopes | 20 |
| Electronic configuration | [Kr] 4d8 5s1 |
| Oxidation states | -1,1,2,3,4,5,6 |
| Electron by energy level | 2,8,18,16,1 |
| Mineral | Hardness | Density |
| Bowieite | 7.00 / 7.00 | |
| Cherepanovite | 6.00 / 6.00 | 9.72 |
| Cuprorhodsite | 5.00 / 5.50 | 6.74 |
| Ferhodsite | ||
| Ferrorhodsite | 4.50 / 4.50 | 5.71 |
| Hollingworthite | 6.00 / 6.50 | 7.91 |
| Irarsite | 6.50 / 6.50 | 11.00 |
| Kashinite | 7.50 / 7.50 | 9.10 |
| Kingstonite | 6.00 / 6.00 | 7.52 |
| Konderite | 5.50 / 5.50 | 4.73 |
| Miassite | 5.50 / 6.00 | |
| Palladodymite | ||
| Platarsite | 7.50 / 7.50 | 8.00 |
| Polkanovite | 10.22 | |
| Rhodarsenide | 4.00 / 5.00 | 11.27 |
| Rhodium | 3.50 / 3.50 | 16.51 |
| Rhodplumsite | 9.00 | |
| Xingzhongite | 6.00 / 6.00 | 6.64 |
| Zaccariniite | 3.50 / 4.00 |
 mineraly.fr
mineraly.fr
 mineraly.co.uk
mineraly.co.uk
 mineraly.com.de
mineraly.com.de
 mineraly.it
mineraly.it
 mineraly.es
mineraly.es
 mineraly.nl
mineraly.nl
 mineraly.pt
mineraly.pt
 mineraly.se
mineraly.se