List of elements
»
Actinium
»
Aluminum
»
Antimony
»
Argon
»
Arsenic
»
astatine
»
Barium
»
Bismuth
»
bohrium
»
Boron
»
Bromine
»
Cadmium
»
Calcium
»
Carbon
»
Cerium
»
cesium
»
Chlorine
»
Chromium
»
Cobalt
»
Copper
»
Curium
»
dubnium
»
Erbium
»
Europium
»
fermium
»
Fluorine
»
francium
»
Gallium
»
Gold
»
Hafnium
»
hassium
»
Helium
»
holmium
»
Hydrogen
»
Indium
»
Iodine
»
Iridium
»
Iron
»
Krypton
»
Lead
»
Lithium
»
lutetium
»
Mercury
»
Neon
»
Nickel
»
Nihonium
»
Niobium
»
Nitrogen
»
nobelium
»
Osmium
»
Oxygen
»
Platinum
»
Polonium
»
Radium
»
Radon
»
Rhenium
»
rhodium
»
Rubidium
»
Samarium
»
scandium
»
Selenium
»
Silicon
»
Silver
»
Sodium
»
Sulfur
»
Tantalum
»
Terbium
»
Thallium
»
Thorium
»
Thulium
»
Tin
»
Titanium
»
Tungsten
»
Uranium
»
Vanadium
»
Xenon
»
Yttrium
»
Zinc
mineralogy
elements
V Vanadium
V - Vanadium - TRANSITION METAL
Vanadium is a chemical element of the family of transition metals, with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a dense and relatively malleable silver-gray solid metal that has a relatively high hardness and density. It has a very high melting point and dissolves slowly in water, but can be dissolved using chemicals.
vanadium is the fifth most abundant element in the earth's crust, but it is rarely present in usable quantities and often associated with other elements. It was discovered in 1830 by Swedish chemist Nils Sefström.
vanadium is widely used in various industrial and commercial applications, especially in the aerospace industry and refining. It is also used as a catalyst in the chemical industry and as an additive in steels to improve their resistance and hardness. In its natural state, vanadium is toxic and should not be inhaled or ingested. Recent studies show that vanadium can help lower cholesterol levels and improve cardiovascular health.
vanadium is an important element for the manufacture and use of fuel batteries. It is also used in the production of alloys for tools and firearms, and for making dye dyes. Other applications include photosynthesis, the production of corrosion inhibitors and the production of catalysts for diesel and gasoline engines.
vanadium is the fifth most abundant element in the earth's crust, but it is rarely present in usable quantities and often associated with other elements. It was discovered in 1830 by Swedish chemist Nils Sefström.
vanadium is widely used in various industrial and commercial applications, especially in the aerospace industry and refining. It is also used as a catalyst in the chemical industry and as an additive in steels to improve their resistance and hardness. In its natural state, vanadium is toxic and should not be inhaled or ingested. Recent studies show that vanadium can help lower cholesterol levels and improve cardiovascular health.
vanadium is an important element for the manufacture and use of fuel batteries. It is also used in the production of alloys for tools and firearms, and for making dye dyes. Other applications include photosynthesis, the production of corrosion inhibitors and the production of catalysts for diesel and gasoline engines.
Synthetic
Radioactive
Liquid
Gaseous
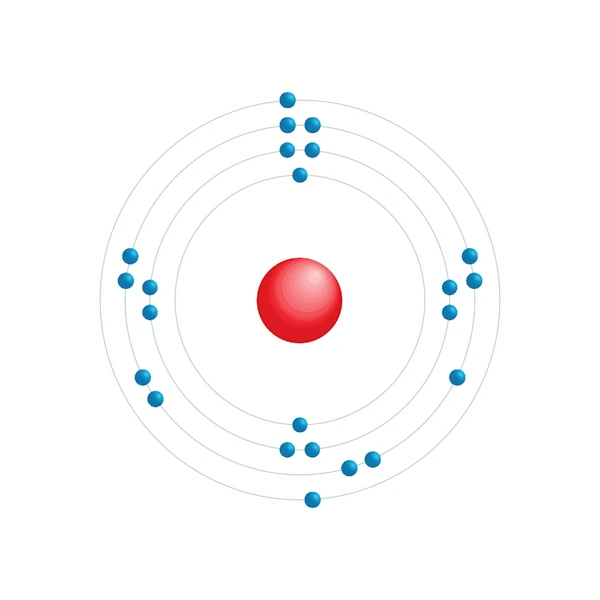
Electronic configuration diagram
| Name | Vanadium |
| Number | 23 |
| Atomic | 50.9415 |
| Symbol | V |
| Fusion | 1890 |
| Boiling | 3380 |
| Density | 6.11 |
| Period | 4 |
| Group | 5 |
| Discovery | 1801 del Rio |
| Abundance | 120 |
| Radius | 1.9 |
| Electronegativity | 1.63 |
| Ionization | 6.7462 |
| Number of isotopes | 9 |
| Electronic configuration | [Ar] 3d3 4s2 |
| Oxidation states | -1,2,3,4 |
| Electron by energy level | 2,8,11,2 |
| Mineral | Hardness | Density |
| Allendeite | 4.84 | |
| Alvanite | 3.00 / 3.50 | 2.41 |
| Andreyivanovite | ||
| Ankangite | 6.50 / 6.50 | 4.44 |
| Ankinovichite | 2.50 / 3.00 | 2.48 |
| Anorthominasragrite | 1.00 / 1.00 | 2.12 |
| Ansermetite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 2.57 |
| Aradite | ||
| Ardennite-(As) | 6.00 / 7.00 | 3.62 |
| Ardennite-(V) | 6.00 / 7.00 | 3.55 |
| Argandite | ||
| Averievite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 3.54 |
| Balestraite | 2.50 / 3.00 | 2.95 |
| Bannermanite | 3.50 | |
| Bariandite | 2.70 | |
| Bariosincosite | 3.00 / 3.00 | |
| Barnesite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 3.15 |
| Bassoite | 4.00 / 4.50 | 2.94 |
| Batisivite | 7.00 / 7.00 | 4.62 |
| Bavsiite | ||
| Beckettite | ||
| Berdesinskiite | 6.00 / 6.50 | |
| Blossite | 3.95 | |
| Bluestreakite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 2.63 |
| Bobjonesite | 1.00 / 1.00 | 2.28 |
| Bokite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 2.97 |
| Borisenkoite | ||
| Brackebuschite | 4.00 / 5.00 | 6.05 |
| Burnettite | ||
| Bushmakinite | 3.00 / 3.50 | 6.22 |
| Byrudite | 7.00 / 7.00 | 4.35 |
| Calciodelrioite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 2.45 |
| Calderónite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 6.05 |
| Calvertite | 4.00 / 5.00 | 5.24 |
| Carnotite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 3.70 |
| Cassagnaite | ||
| Cassedanneite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 6.00 |
| Cavansite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 2.21 |
| Cavoite | ||
| Cechite | 4.50 / 5.00 | 5.88 |
| Cheremnykhite | 5.50 / 5.50 | 6.00 |
| Chernykhite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 3.14 |
| Chervetite | 2.00 / 2.50 | 6.30 |
| Cleusonite | 6.00 / 7.00 | 4.74 |
| Clinobisvanite | 6.95 | |
| Cloncurryite | 2.00 / 2.00 | |
| Colimaite | 2.24 | |
| Colusite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 4.20 |
| Coparsite | ||
| Coronadite | 4.50 / 5.00 | 5.44 |
| Cortesognoite | ||
| Corvusite | 2.50 / 3.00 | 2.82 |
| Coulsonite | 4.50 / 5.00 | 5.17 |
| Crichtonite | 5.00 / 6.00 | 4.46 |
| Curienite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 4.88 |
| Davidite-(Ce) | 6.00 / 6.00 | 4.42 |
| Davidite-(La) | 6.00 / 6.00 | 4.42 |
| Davisite | ||
| Delrioite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 3.10 |
| Descloizite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 6.10 |
| Dessauite-(Y) | 6.50 / 7.00 | 4.68 |
| Dickthomssenite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 1.96 |
| Dissakisite-(La) | 6.50 / 7.00 | 3.79 |
| Doloresite | 3.27 | |
| Dreyerite | 2.00 / 3.00 | 6.25 |
| Dugganite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 6.33 |
| Duttonite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 3.24 |
| Engelhauptite | 3.86 | |
| Erlianite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 3.11 |
| Evdokimovite | ||
| Fernandinite | 2.00 / 3.00 | 2.78 |
| Ferribushmakinite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 6.15 |
| Fervanite | 3.28 | |
| Fianelite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 3.21 |
| Fingerite | ||
| Francevillite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 4.55 |
| Franciscanite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 4.00 |
| Fritzscheite | 2.00 / 3.00 | 4.39 |
| Gamagarite | 4.50 / 5.00 | 4.62 |
| Gatewayite | ||
| Germanocolusite | 4.50 / 5.00 | 4.00 |
| Goldmanite | 6.00 / 7.00 | 3.74 |
| Goldquarryite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 2.78 |
| Gottlobite | 4.50 / 4.50 | 3.41 |
| Gramaccioliite-(Y) | 6.00 / 6.00 | 4.66 |
| Grantsite | 1.00 / 2.00 | 2.94 |
| Greenwoodite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 4.81 |
| Grigorievite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 3.67 |
| Gunterite | 1.00 / 1.00 | 2.40 |
| Gurimite | ||
| Häggite | 4.50 / 4.50 | 3.00 |
| Hanjiangite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 3.78 |
| Haradaite | 4.50 / 4.50 | 3.80 |
| Hechtsbergite | 4.50 / 4.50 | 6.87 |
| Hemloite | 6.50 / 6.50 | 4.00 |
| Hendersonite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 2.77 |
| Hereroite | 8.15 | |
| Hewettite | 2.50 | |
| Heyite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 6.30 |
 mineraly.fr
mineraly.fr
 mineraly.co.uk
mineraly.co.uk
 mineraly.com.de
mineraly.com.de
 mineraly.it
mineraly.it
 mineraly.es
mineraly.es
 mineraly.nl
mineraly.nl
 mineraly.pt
mineraly.pt
 mineraly.se
mineraly.se