List of elements
»
Actinium
»
Aluminum
»
Antimony
»
Argon
»
Arsenic
»
astatine
»
Barium
»
Bismuth
»
bohrium
»
Boron
»
Bromine
»
Cadmium
»
Calcium
»
Carbon
»
Cerium
»
cesium
»
Chlorine
»
Chromium
»
Cobalt
»
Copper
»
Curium
»
dubnium
»
Erbium
»
Europium
»
fermium
»
Fluorine
»
francium
»
Gallium
»
Gold
»
Hafnium
»
hassium
»
Helium
»
holmium
»
Hydrogen
»
Indium
»
Iodine
»
Iridium
»
Iron
»
Krypton
»
Lead
»
Lithium
»
lutetium
»
Mercury
»
Neon
»
Nickel
»
Nihonium
»
Niobium
»
Nitrogen
»
nobelium
»
Osmium
»
Oxygen
»
Platinum
»
Polonium
»
Radium
»
Radon
»
Rhenium
»
rhodium
»
Rubidium
»
Samarium
»
scandium
»
Selenium
»
Silicon
»
Silver
»
Sodium
»
Sulfur
»
Tantalum
»
Terbium
»
Thallium
»
Thorium
»
Thulium
»
Tin
»
Titanium
»
Tungsten
»
Uranium
»
Vanadium
»
Xenon
»
Yttrium
»
Zinc
mineralogy
elements
N Nitrogen
N - Nitrogen - OTHER NO METAL
Nitrogen is a chemical element of the family of non-metals present in the atmosphere of the Earth. Its gaseous form represents about 78% of the atmosphere and the rest is composed of oxygen.
nitrogen is a colorless chemical element (in gaseous state) that is found as an odorless and tasteless gas. Its atomic number is 7 and its atomic mass is 14. Under normal conditions, nitrogen gas is a diatomic compound, that is, it is in the form of two N atoms bonded by a covalent bond.
nitrogen is widely used in industry due to its unique chemical properties. It exists in two forms, one in gaseous form and one in liquid form. In its liquid form, it is used as a cooler. In addition to its cooling properties, it is also used as an inert gas because it does not interact with any other chemical compound and does not react easily with other elements.
nitrogen is widely used in various industries. It is used for cooling and preserving food. It is also used as an inert gas during certain industrial operations. It is also used as a soporific gas during anesthesia and as a propellant gas in certain types of rockets. It is also used as purge and fill gas. Finally, nitrogen is used to purify the interior of bottles and containers containing flammable chemicals.
nitrogen is a colorless chemical element (in gaseous state) that is found as an odorless and tasteless gas. Its atomic number is 7 and its atomic mass is 14. Under normal conditions, nitrogen gas is a diatomic compound, that is, it is in the form of two N atoms bonded by a covalent bond.
nitrogen is widely used in industry due to its unique chemical properties. It exists in two forms, one in gaseous form and one in liquid form. In its liquid form, it is used as a cooler. In addition to its cooling properties, it is also used as an inert gas because it does not interact with any other chemical compound and does not react easily with other elements.
nitrogen is widely used in various industries. It is used for cooling and preserving food. It is also used as an inert gas during certain industrial operations. It is also used as a soporific gas during anesthesia and as a propellant gas in certain types of rockets. It is also used as purge and fill gas. Finally, nitrogen is used to purify the interior of bottles and containers containing flammable chemicals.
Synthetic
Radioactive
Liquid
Gaseous
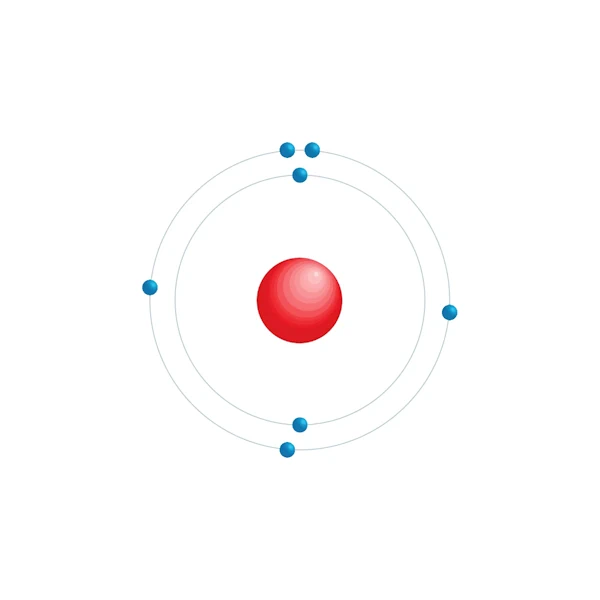
Electronic configuration diagram
| Name | Nitrogen |
| Number | 7 |
| Atomic | 14.0072 |
| Symbol | N |
| Fusion | -209.9 |
| Boiling | -195.8 |
| Density | 0.0012506 |
| Period | 2 |
| Group | 15 |
| Discovery | 1772 Rutherford |
| Abundance | 19 |
| Radius | 0.75 |
| Electronegativity | 3.04 |
| Ionization | 14.5341 |
| Number of isotopes | 8 |
| Electronic configuration | [He] 2s2 2p3 |
| Oxidation states | -3,-2,-1,1,2,3,4,5 |
| Electron by energy level | 2,5 |
| Mineral | Hardness | Density |
| Abelsonite | 2.00 / 2.50 | 1.45 |
| Acetamide | 1.00 / 1.50 | 1.17 |
| Acmonidesite | ||
| Adranosite | ||
| Adranosite-(Fe) | 2.20 | |
| Aluminopyracmonite | 2.14 | |
| Ambrinoite | 3.31 | |
| Ammineite | ||
| Ammonioalunite | 2.00 / 3.00 | 2.40 |
| Ammonioborite | 1.77 | |
| Ammoniojarosite | 3.50 / 4.50 | 3.02 |
| Ammonioleucite | 5.50 / 6.00 | 2.29 |
| Ammoniomagnesiovoltaite | ||
| Archerite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 2.00 |
| Argesite | 2.84 | |
| Bararite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 2.15 |
| Barberiite | 1.00 / 1.00 | 1.89 |
| Beshtauite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 3.05 |
| Biphosphammite | 1.00 / 2.00 | 2.04 |
| Boussingaultite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 1.70 |
| Brontesite | 2.73 | |
| Buddingtonite | 5.50 / 5.50 | 2.32 |
| Buttgenbachite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 3.42 |
| Campostriniite | 3.87 | |
| Carlsbergite | 7.00 / 7.00 | 5.90 |
| Carlsonite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 2.17 |
| Chanabayaite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 1.46 |
| Clairite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 2.31 |
| Comancheite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 7.70 |
| Cryptohalite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 2.01 |
| Darapskite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 2.20 |
| Dendritic Opal | 5.50 / 6.50 | 2.15 |
| Dittmarite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.19 |
| Efremovite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 2.00 |
| Gerhardtite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 3.40 |
| Gianellaite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 7.19 |
| Godovikovite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 2.53 |
| Guanine | 1.00 / 2.00 | 1.49 |
| Gwihabaite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 1.77 |
| Hannayite | 2.00 / 3.00 | 2.03 |
| Huizingite-(Al) | 2.50 / 2.50 | 2.03 |
| Humberstonite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 2.25 |
| Hydrombobomkulite | ||
| Joanneumite | 1.00 / 1.00 | 2.02 |
| Julienite | 1.65 | |
| Kafehydrocyanite | 2.00 / 2.50 | 1.98 |
| Kladnoite | 1.47 | |
| Kleinite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 8.00 |
| Koktaite | 2.09 | |
| Kremersite | 2.17 | |
| Larderellite | 1.00 / 2.00 | 1.91 |
| Lecontite | 2.00 / 2.50 | 1.75 |
| Letovicite | 1.00 / 2.00 | 1.83 |
| Likasite | 2.96 | |
| Lislkirchnerite | ||
| Lonecreekite | 2.00 / 3.00 | 1.69 |
| Lucabindiite | 3.68 | |
| Mascagnite | 2.00 / 2.50 | 1.77 |
| Mbobomkulite | 2.30 | |
| Metauramphite | ||
| Möhnite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 2.46 |
| Mohrite | 2.00 / 2.50 | 1.80 |
| Mosesite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 7.72 |
| Mundrabillaite | 1.00 / 2.00 | 2.05 |
| Niahite | 1.00 / 2.00 | 2.39 |
| Nickelalumite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 2.24 |
| Nickelboussingaultite | 2.50 / 2.50 | |
| Nierite | 9.00 / 9.00 | 3.17 |
| Niter | 2.00 / 2.00 | 2.10 |
| Nitratine | 1.50 / 2.00 | 2.24 |
| Nitrobarite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 3.25 |
| Nitrocalcite | 1.00 / 2.00 | 1.90 |
| Nitromagnesite | 1.58 | |
| Osbornite | 8.50 / 8.50 | 5.00 |
| Oxammite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 1.50 |
| Panichiite | 2.43 | |
| Phosphammite | 1.00 / 1.00 | 1.33 |
| Pyracmonite | 2.23 | |
| Qingsongite | 9.00 / 10.00 | 3.46 |
| Roaldite | 5.50 / 6.50 | 7.21 |
| Rouaite | 3.38 | |
| Russoite | ||
| Sabieite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 2.68 |
| Salammoniac | 1.50 / 2.00 | 1.50 |
| Schertelite | 1.83 | |
| Schindlerite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 2.46 |
| Shilovite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 1.92 |
| Siderazot | 3.15 | |
| Sinoite | 2.80 | |
| Spheniscidite | 1.00 / 1.50 | 2.71 |
| Stercorite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 1.55 |
| Struvite | 1.50 / 2.00 | 1.70 |
| Suhailite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 2.95 |
| Sveite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 2.00 |
| Swaknoite | 1.50 / 2.00 | 1.91 |
| Teschemacherite | 1.50 / 1.50 | 1.58 |
| Therasiaite | 2.40 | |
| Thermessaite-(NH4) | ||
| Tinnunculite | 1.73 |
 mineraly.fr
mineraly.fr
 mineraly.co.uk
mineraly.co.uk
 mineraly.com.de
mineraly.com.de
 mineraly.it
mineraly.it
 mineraly.es
mineraly.es
 mineraly.nl
mineraly.nl
 mineraly.pt
mineraly.pt
 mineraly.se
mineraly.se