List of elements
»
Actinium
»
Aluminum
»
Antimony
»
Argon
»
Arsenic
»
astatine
»
Barium
»
Bismuth
»
bohrium
»
Boron
»
Bromine
»
Cadmium
»
Calcium
»
Carbon
»
Cerium
»
cesium
»
Chlorine
»
Chromium
»
Cobalt
»
Copper
»
Curium
»
dubnium
»
Erbium
»
Europium
»
fermium
»
Fluorine
»
francium
»
Gallium
»
Gold
»
Hafnium
»
hassium
»
Helium
»
holmium
»
Hydrogen
»
Indium
»
Iodine
»
Iridium
»
Iron
»
Krypton
»
Lead
»
Lithium
»
lutetium
»
Mercury
»
Neon
»
Nickel
»
Nihonium
»
Niobium
»
Nitrogen
»
nobelium
»
Osmium
»
Oxygen
»
Platinum
»
Polonium
»
Radium
»
Radon
»
Rhenium
»
rhodium
»
Rubidium
»
Samarium
»
scandium
»
Selenium
»
Silicon
»
Silver
»
Sodium
»
Sulfur
»
Tantalum
»
Terbium
»
Thallium
»
Thorium
»
Thulium
»
Tin
»
Titanium
»
Tungsten
»
Uranium
»
Vanadium
»
Xenon
»
Yttrium
»
Zinc
O - Oxygen - OTHER NO METAL
Oxygen (chemical symbol O) is a chemical element of the chalcogen family, subgroup 16 of the periodic table of elements. It is the major component of the Earth's atmosphere, representing about 20.9% of the total volume.
oxygen is a very reactive compound and therefore very important for many chemical reactions. It is the 3rd most abundant element in the universe after hydrogen and helium. It is able to form covalent bonds with other atoms and can combine with them to form more complex molecules such as organic compounds. oxygen is a gas in its normal state, it is a colorless, odorless and tasteless gas. Its chemical formula is O2 and its molar mass is 32 g/mol.
oxygen is a very reactive gas since it has eight electrons in its outer electron shell. It is a strong oxidant and is very useful in various chemical reactions. It is also very soluble in water and is the main source of oxygen available to living things. oxygen is also combustible and is heavily used in industries and laboratories for its oxidizing properties.
oxygen is the main component of fossil fuels and is therefore very important in the combustion process. It is widely used for various industrial applications including the manufacture of metals, chemicals, fertilizers, drugs and pharmaceuticals. In addition to industrial uses, oxygen is used in medical treatment to help people with serious respiratory illnesses. It is also used by many industries such as aeronautics, astronautics and extreme sports.
oxygen is a very reactive compound and therefore very important for many chemical reactions. It is the 3rd most abundant element in the universe after hydrogen and helium. It is able to form covalent bonds with other atoms and can combine with them to form more complex molecules such as organic compounds. oxygen is a gas in its normal state, it is a colorless, odorless and tasteless gas. Its chemical formula is O2 and its molar mass is 32 g/mol.
oxygen is a very reactive gas since it has eight electrons in its outer electron shell. It is a strong oxidant and is very useful in various chemical reactions. It is also very soluble in water and is the main source of oxygen available to living things. oxygen is also combustible and is heavily used in industries and laboratories for its oxidizing properties.
oxygen is the main component of fossil fuels and is therefore very important in the combustion process. It is widely used for various industrial applications including the manufacture of metals, chemicals, fertilizers, drugs and pharmaceuticals. In addition to industrial uses, oxygen is used in medical treatment to help people with serious respiratory illnesses. It is also used by many industries such as aeronautics, astronautics and extreme sports.
Synthetic
Radioactive
Liquid
Gaseous
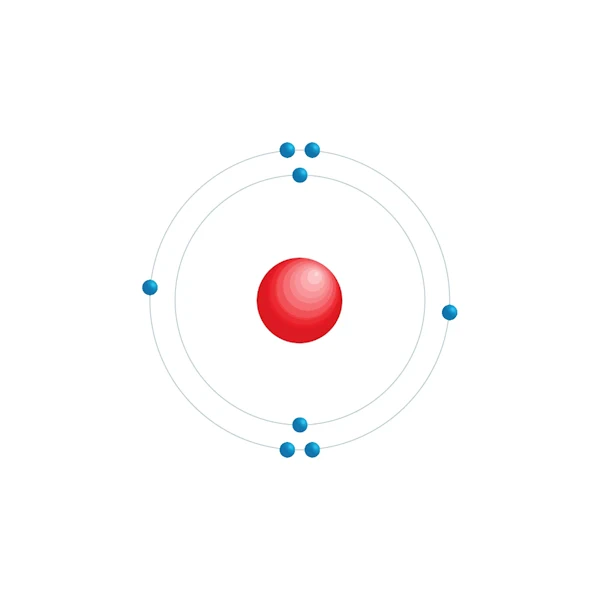
Electronic configuration diagram
| Name | Oxygen |
| Number | 8 |
| Atomic | 15.9992 |
| Symbol | O |
| Fusion | -218.4 |
| Boiling | -182.9 |
| Density | 0.001429 |
| Period | 2 |
| Group | 16 |
| Discovery | 1774 Priestley/Scheele |
| Abundance | 461000 |
| Radius | 0.65 |
| Electronegativity | 3.44 |
| Ionization | 13.6181 |
| Number of isotopes | 8 |
| Electronic configuration | [He] 2s2 2p4 |
| Oxidation states | -2,-1,1,2 |
| Electron by energy level | 2,6 |
| Mineral | Hardness | Density |
| Abenakiite-(Ce) | 4.00 / 4.00 | 3.21 |
| Abernathyite | 2.00 / 3.00 | 3.31 |
| Abhurite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 4.29 |
| Abswurmbachite | 6.50 / 6.50 | 4.96 |
| Abuite | ||
| Acetamide | 1.00 / 1.50 | 1.17 |
| Achalaite | ||
| Acmonidesite | ||
| Actinolite | 5.50 / 5.50 | 2.98 |
| Acuminite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 3.30 |
| Adachiite | ||
| Adamite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 4.30 |
| Adamsite-(Y) | 3.00 / 3.00 | |
| Addibischoffite | ||
| Adelite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 3.73 |
| Admontite | 2.00 / 3.00 | 1.82 |
| Adolfpateraite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 4.24 |
| Adranosite | ||
| Adranosite-(Fe) | 2.20 | |
| Adrianite | ||
| Aegirine | 6.00 / 6.50 | 3.50 |
| Aegirine-augite | 6.00 / 6.00 | 3.40 |
| Aenigmatite | 5.00 / 6.00 | 3.74 |
| Aerinite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 2.48 |
| Aerugite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 5.85 |
| Aeschynite-(Ce) | 5.00 / 6.00 | 5.19 |
| Aeschynite-(Nd) | 5.00 / 6.00 | 4.60 |
| Aeschynite-(Y) | 5.00 / 6.00 | 4.85 |
| Afghanite | 5.50 / 6.00 | 2.55 |
| Afmite | ||
| Afwillite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 2.62 |
| Agaite | 6.99 | |
| Agakhanovite-(Y) | 6.00 / 6.00 | 2.67 |
| Agardite-(Ce) | 3.00 / 3.00 | 3.72 |
| Agardite-(La) | 3.00 / 4.00 | 3.72 |
| Agardite-(Nd) | 3.00 / 4.00 | 3.72 |
| Agardite-(Y) | 3.00 / 4.00 | 3.66 |
| Agate | 6.50 / 7.00 | 2.60 |
| Agrellite | 5.50 / 5.50 | 2.88 |
| Agricolaite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 3.53 |
| Agrinierite | 5.62 | |
| Aheylite | 5.00 / 6.00 | 2.85 |
| Ahlfeldite | 2.00 / 2.50 | 3.37 |
| Ahrensite | 4.14 | |
| Aiolosite | 3.59 | |
| Ajoite | 2.96 | |
| Akaganeite | 3.00 | |
| Akaogiite | ||
| Akatoreite | 6.00 / 6.00 | 3.48 |
| Akdalaite | 7.00 / 7.00 | 3.68 |
| Akermanite | 5.00 / 6.00 | 2.94 |
| Akhtenskite | 4.00 | |
| Akimotoite | ||
| Aklimaite | ||
| Akrochordite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 3.19 |
| Aksaite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 1.99 |
| Alamosite | 4.50 / 4.50 | 6.49 |
| Alarsite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 3.32 |
| Albertiniite | 2.46 | |
| Albite | 7.00 / 7.00 | 2.61 |
| Albrechtschraufite | 2.00 / 3.00 | 2.60 |
| Alcaparrosaite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 2.81 |
| Aldermanite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 2.00 |
| Aldridgeite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 3.33 |
| Aleksandrovite | 4.00 / 4.50 | 3.07 |
| Alexkhomyakovite | ||
| Alflarsenite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 2.61 |
| Alforsite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 4.73 |
| Alfredopetrovite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 2.50 |
| Alfredstelznerite | ||
| Aliettite | 1.00 / 2.00 | |
| Allactite | 4.50 / 4.50 | 3.00 |
| Allanite-(Ce) | 5.50 / 5.50 | 3.30 |
| Allanite-(La) | 6.00 / 6.00 | 3.93 |
| Allanite-(Nd) | ||
| Allanite-(Y) | 5.50 / 5.50 | 3.30 |
| Allanpringite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 2.54 |
| Alleghanyite | 6.00 / 5.00 | 4.00 |
| Allendeite | 4.84 | |
| Allochalcoselite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 4.65 |
| Allophane | 3.00 / 3.00 | 1.90 |
| Alloriite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.35 |
| Alluaivite | 5.00 / 6.00 | 2.76 |
| Alluaudite | 5.00 / 5.50 | 3.45 |
| Almandine | 7.00 / 8.00 | 4.09 |
| Almarudite | 6.00 / 6.00 | 2.71 |
| Almeidaite | ||
| Alnaperbøeite-(Ce) | ||
| Alpersite | 2.50 / 2.50 | |
| Alsakharovite-Zn | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.90 |
| Alstonite | 4.00 / 4.50 | 3.69 |
| Althausite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 2.97 |
| Althupite | 3.50 / 4.00 | 3.90 |
| Altisite | 6.00 / 6.00 | 2.64 |
| Alum-(K) | 2.00 / 2.00 | 1.76 |
| Alum-(Na) | 3.00 / 3.00 | 1.67 |
| Aluminite | 1.00 / 1.00 | 1.66 |
| Alumino-ferrobarroisite | ||
| Alumino-ferrohornblende |
 mineraly.fr
mineraly.fr
 mineraly.co.uk
mineraly.co.uk
 mineraly.com.de
mineraly.com.de
 mineraly.it
mineraly.it
 mineraly.es
mineraly.es
 mineraly.nl
mineraly.nl
 mineraly.pt
mineraly.pt
 mineraly.se
mineraly.se