List of elements
»
Actinium
»
Aluminum
»
Antimony
»
Argon
»
Arsenic
»
astatine
»
Barium
»
Bismuth
»
bohrium
»
Boron
»
Bromine
»
Cadmium
»
Calcium
»
Carbon
»
Cerium
»
cesium
»
Chlorine
»
Chromium
»
Cobalt
»
Copper
»
Curium
»
dubnium
»
Erbium
»
Europium
»
fermium
»
Fluorine
»
francium
»
Gallium
»
Gold
»
Hafnium
»
hassium
»
Helium
»
holmium
»
Hydrogen
»
Indium
»
Iodine
»
Iridium
»
Iron
»
Krypton
»
Lead
»
Lithium
»
lutetium
»
Mercury
»
Neon
»
Nickel
»
Nihonium
»
Niobium
»
Nitrogen
»
nobelium
»
Osmium
»
Oxygen
»
Platinum
»
Polonium
»
Radium
»
Radon
»
Rhenium
»
rhodium
»
Rubidium
»
Samarium
»
scandium
»
Selenium
»
Silicon
»
Silver
»
Sodium
»
Sulfur
»
Tantalum
»
Terbium
»
Thallium
»
Thorium
»
Thulium
»
Tin
»
Titanium
»
Tungsten
»
Uranium
»
Vanadium
»
Xenon
»
Yttrium
»
Zinc
mineralogy
elements
Zr Zirconium
Zr - Zirconium - TRANSITION METAL
Zirconium is a metallic chemical element of the family of transition metals belonging to group 4 of the periodic table and having the atomic number 40 and the symbol Zr. This element is worked in order to obtain increased resistance, a low expansion coefficient, a high resistance to corrosion and a low density.
zirconium is a very light metal and one of the most reactive transition metals. Its color is white and its density is approximately 6.5 g/cm3. zirconium is also highly resistant to oxidation and corrosion by seawater and other chemically aggressive media. It is very malleable and can be formed and welded at relatively low temperatures.
zirconium has a strong ability to absorb neutrons and is therefore commonly used to build the core of nuclear reactors. zirconium is also an excellent conductor of heat and can be used to make pipes and heat reflectors. In addition, zirconium is a material of choice for manufacturing electrical wires and cables because it is highly resistant to electrochemical corrosion.
The main uses of zirconium are in the nuclear industry and the automotive sector. It is mainly used for the manufacture of various engine components and parts, including exhaust manifolds, inductors and valves. zirconium is also used in the chemical and pharmaceutical industry and is commonly used to make filters, bottles and tubes for the production of chemicals. Its use is also widespread in the aerospace and defense industry, especially for the manufacture of tanks and aircraft parts, and for the manufacture of electronic components such as capacitors, resistors and transformer windings.
zirconium is a very light metal and one of the most reactive transition metals. Its color is white and its density is approximately 6.5 g/cm3. zirconium is also highly resistant to oxidation and corrosion by seawater and other chemically aggressive media. It is very malleable and can be formed and welded at relatively low temperatures.
zirconium has a strong ability to absorb neutrons and is therefore commonly used to build the core of nuclear reactors. zirconium is also an excellent conductor of heat and can be used to make pipes and heat reflectors. In addition, zirconium is a material of choice for manufacturing electrical wires and cables because it is highly resistant to electrochemical corrosion.
The main uses of zirconium are in the nuclear industry and the automotive sector. It is mainly used for the manufacture of various engine components and parts, including exhaust manifolds, inductors and valves. zirconium is also used in the chemical and pharmaceutical industry and is commonly used to make filters, bottles and tubes for the production of chemicals. Its use is also widespread in the aerospace and defense industry, especially for the manufacture of tanks and aircraft parts, and for the manufacture of electronic components such as capacitors, resistors and transformer windings.
Synthetic
Radioactive
Liquid
Gaseous
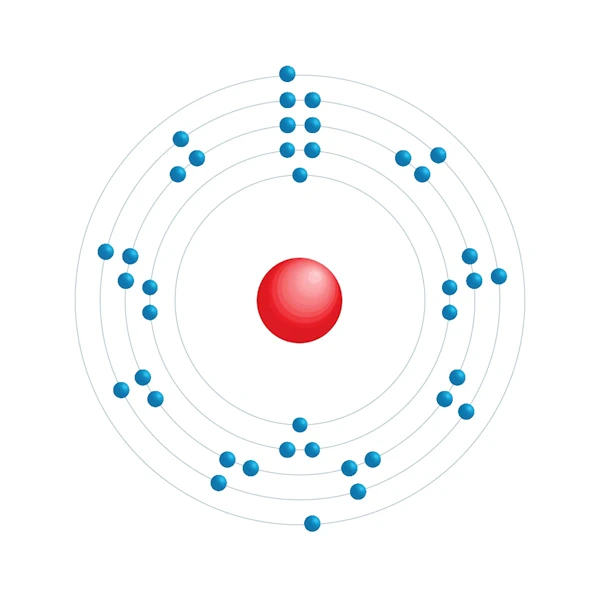
Electronic configuration diagram
| Name | Zirconium |
| Number | 40 |
| Atomic | 91.224 |
| Symbol | Zr |
| Fusion | 1852 |
| Boiling | 4377 |
| Density | 6.506 |
| Period | 5 |
| Group | 4 |
| Discovery | 1789 Klaproth |
| Abundance | 165 |
| Radius | 2.2 |
| Electronegativity | 1.33 |
| Ionization | 6.6339 |
| Number of isotopes | 20 |
| Electronic configuration | [Kr] 4d2 5s2 |
| Oxidation states | 1,2,3,4 |
| Electron by energy level | 2,8,18,10,2 |
| Mineral | Hardness | Density |
| Aenigmatite | 5.00 / 6.00 | 3.74 |
| Allendeite | 4.84 | |
| Andrianovite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 3.02 |
| Aqualite | 4.00 / 5.00 | 2.66 |
| Armstrongite | 4.50 / 4.50 | 2.70 |
| Baddeleyite | 6.50 / 6.50 | 5.50 |
| Baghdadite | 6.00 / 6.00 | 3.48 |
| Baratovite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 2.92 |
| Bazirite | 6.00 / 6.50 | 3.82 |
| Belyankinite | 2.00 / 3.00 | 2.32 |
| Bobtraillite | 5.50 / 5.50 | 3.16 |
| Burpalite | 5.00 / 6.00 | 3.33 |
| Calciocatapleiite | 4.50 / 5.00 | 2.77 |
| Calciohilairite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 2.68 |
| Calzirtite | 6.00 / 7.00 | 5.01 |
| Carbokentbrooksite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 3.14 |
| Catapleiite | 6.00 / 6.00 | 2.75 |
| Ceriopyrochlore-(Ce) | 5.00 / 5.50 | 4.13 |
| Dalyite | 7.50 / 7.50 | 2.84 |
| Darapiosite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.92 |
| Davinciite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.85 |
| Davisite | ||
| Dovyrenite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 3.03 |
| Dualite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.84 |
| Dusmatovite | 4.50 / 4.50 | 2.96 |
| Elbrusite | ||
| Ellenbergerite | 6.50 / 6.50 | 3.15 |
| Elpidite | 7.00 / 7.00 | 2.54 |
| Eudialyte | 5.00 / 5.50 | 2.80 |
| Eveslogite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.85 |
| Feklichevite | 5.50 / 5.50 | 2.87 |
| Fengchengite | ||
| Ferrokentbrooksite | 5.00 / 6.00 | 3.06 |
| Gaidonnayite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.67 |
| Gainesite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 2.94 |
| Gatedalite | 4.78 | |
| Georgbarsanovite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 3.05 |
| Georgechaoite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.70 |
| Gittinsite | 3.50 / 4.00 | 3.62 |
| Golyshevite | 5.50 / 5.50 | 2.89 |
| Grenmarite | 4.50 / 4.50 | 3.49 |
| Gutkovaite-Mn | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.83 |
| Hafnon | 7.50 / 7.50 | 6.97 |
| Haineaultite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 2.28 |
| Hainite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 3.15 |
| Hezuolinite | 5.50 / 6.00 | 4.30 |
| Hiärneite | 7.00 / 7.00 | 5.44 |
| Hilairite | 4.50 / 4.50 | 2.72 |
| Hiortdahlite | 5.50 / 5.50 | 3.27 |
| Hydroterskite | ||
| Ikranite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.82 |
| Ilyukhinite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.70 |
| Janhaugite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 3.60 |
| Jinshajiangite | 4.50 / 5.00 | 3.61 |
| Johnsenite-(Ce) | 5.00 / 6.00 | 3.20 |
| Kapustinite | 6.00 / 6.00 | 2.78 |
| Keldyshite | 3.50 / 4.50 | 3.30 |
| Kentbrooksite | 5.00 / 6.00 | 3.07 |
| Kerimasite | 7.00 / 7.00 | 4.11 |
| Khibinskite | 4.50 / 5.50 | 3.30 |
| Khomyakovite | 5.00 / 6.00 | 3.14 |
| Kimzeyite | 7.00 / 7.00 | 4.00 |
| Kochite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 3.32 |
| Komkovite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 3.31 |
| Kosnarite | 4.50 / 4.50 | 3.19 |
| Kostylevite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.74 |
| Kristiansenite | 5.50 / 6.00 | 3.30 |
| Laachite | 5.42 | |
| Labyrinthite | 5.00 / 6.00 | 2.88 |
| Lakargiite | 8.00 / 8.50 | 4.59 |
| Låvenite | 6.00 / 6.00 | 3.51 |
| Lemoynite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 2.29 |
| Lindsleyite | 7.50 / 7.50 | 4.63 |
| Litvinskite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.61 |
| Loranskite-(Y) | 5.00 / 5.00 | 4.40 |
| Loudounite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.48 |
| Loveringite | 7.50 / 7.50 | 4.41 |
| Lovozerite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.30 |
| Malhmoodite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 2.88 |
| Manganoeudialyte | 5.00 / 6.00 | 2.89 |
| Manganokhomyakovite | 5.00 / 6.00 | 3.13 |
| Marianoite | 6.00 / 6.00 | 3.32 |
| Mathiasite | 7.50 / 7.50 | 4.60 |
| Mccrillisite | 4.50 / 4.50 | 3.12 |
| Menezesite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 4.18 |
| Mogovidite | 5.50 / 5.50 | 2.90 |
| Mongshanite | 5.00 / 6.00 | |
| Mosandrite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 3.29 |
| Nalivkinite | 3.29 | |
| Natrolemoynite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 2.47 |
| Niobokupletskite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 3.33 |
| Normandite | 5.00 / 6.00 | 3.48 |
| Oneillite | 5.00 / 6.00 | 3.20 |
| Painite | 8.00 / 8.00 | 4.00 |
| Panguite | 3.75 | |
| Parakeldyshite | 5.50 / 6.00 | 3.39 |
| Paraumbite | 4.50 / 4.50 | 2.59 |
| Penkvilksite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.63 |
| Petarasite | 5.00 / 5.50 | 2.88 |
 mineraly.fr
mineraly.fr
 mineraly.co.uk
mineraly.co.uk
 mineraly.com.de
mineraly.com.de
 mineraly.it
mineraly.it
 mineraly.es
mineraly.es
 mineraly.nl
mineraly.nl
 mineraly.pt
mineraly.pt
 mineraly.se
mineraly.se