List of elements
»
Actinium
»
Aluminum
»
Antimony
»
Argon
»
Arsenic
»
astatine
»
Barium
»
Bismuth
»
bohrium
»
Boron
»
Bromine
»
Cadmium
»
Calcium
»
Carbon
»
Cerium
»
cesium
»
Chlorine
»
Chromium
»
Cobalt
»
Copper
»
Curium
»
dubnium
»
Erbium
»
Europium
»
fermium
»
Fluorine
»
francium
»
Gallium
»
Gold
»
Hafnium
»
hassium
»
Helium
»
holmium
»
Hydrogen
»
Indium
»
Iodine
»
Iridium
»
Iron
»
Krypton
»
Lead
»
Lithium
»
lutetium
»
Mercury
»
Neon
»
Nickel
»
Nihonium
»
Niobium
»
Nitrogen
»
nobelium
»
Osmium
»
Oxygen
»
Platinum
»
Polonium
»
Radium
»
Radon
»
Rhenium
»
rhodium
»
Rubidium
»
Samarium
»
scandium
»
Selenium
»
Silicon
»
Silver
»
Sodium
»
Sulfur
»
Tantalum
»
Terbium
»
Thallium
»
Thorium
»
Thulium
»
Tin
»
Titanium
»
Tungsten
»
Uranium
»
Vanadium
»
Xenon
»
Yttrium
»
Zinc
mineralogy
elements
Pd Palladium
Pd - Palladium - TRANSITION METAL
Palladium is a silvery-white precious metal from the platinum group metal family. It is the fifth most abundant metal in the earth's crust. Its density is slightly lower than that of gold and silver and its hardness is lower than that of platinum.
palladium has a melting point of 1554°C and a boiling point of 2824°C. Its atomic number is 46 with an atomic weight of 106. It is slightly denser than gold and silver and has a hardness of 4 to 4.5 in Moh making it slightly softer than platinum.
palladium is a very malleable and very ductile silvery-white metal. It is also very stable and resistant to corrosion and oxidation and is very insensitive to water and most chemicals. It is also stable in air at temperatures below 370°C, but oxidizes at higher temperatures.
palladium is mainly used for the manufacture of jewelry and decorative objects and art but it is also used for the manufacture of catalysts, pharmaceutical compounds, capacitors, radiation detectors and electronic compounds. It is also used for the manufacture of catalysts in the automotive industry and in the chemical industry and for the purification of gases.
palladium has a melting point of 1554°C and a boiling point of 2824°C. Its atomic number is 46 with an atomic weight of 106. It is slightly denser than gold and silver and has a hardness of 4 to 4.5 in Moh making it slightly softer than platinum.
palladium is a very malleable and very ductile silvery-white metal. It is also very stable and resistant to corrosion and oxidation and is very insensitive to water and most chemicals. It is also stable in air at temperatures below 370°C, but oxidizes at higher temperatures.
palladium is mainly used for the manufacture of jewelry and decorative objects and art but it is also used for the manufacture of catalysts, pharmaceutical compounds, capacitors, radiation detectors and electronic compounds. It is also used for the manufacture of catalysts in the automotive industry and in the chemical industry and for the purification of gases.
Synthetic
Radioactive
Liquid
Gaseous
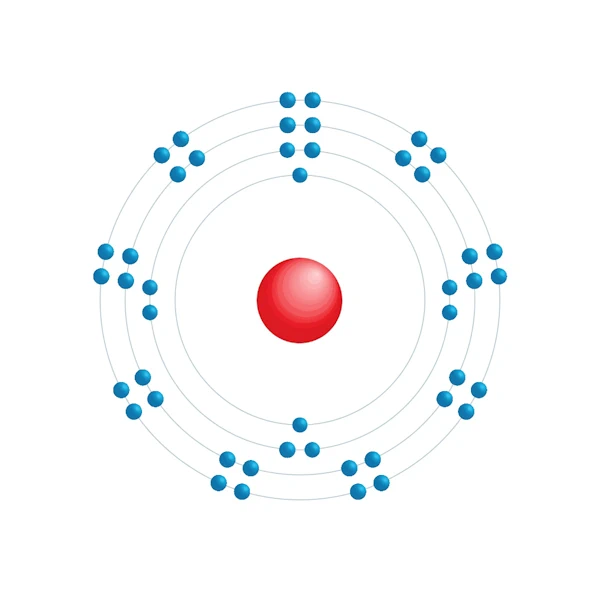
Electronic configuration diagram
| Name | Palladium |
| Number | 46 |
| Atomic | 106.42 |
| Symbol | Pd |
| Fusion | 1552 |
| Boiling | 3140 |
| Density | 12.02 |
| Period | 5 |
| Group | 10 |
| Discovery | 1803 Wollaston |
| Abundance | 0.015 |
| Radius | 1.8 |
| Electronegativity | 2.2 |
| Ionization | 8.3369 |
| Number of isotopes | 21 |
| Electronic configuration | [Kr] 4d10 |
| Oxidation states | 2,4 |
| Electron by energy level | 2,8,18,18 |
| Mineral | Hardness | Density |
| Arsenopalladinite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 10.40 |
| Atheneite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 10.20 |
| Atokite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 14.90 |
| Borishanskiite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 10.00 |
| Borovskite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 8.12 |
| Bortnikovite | 4.50 / 5.00 | 11.16 |
| Braggite | 1.50 / 1.50 | 10.00 |
| Cabriite | 4.00 / 4.50 | 10.70 |
| Chrisstanleyite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 8.31 |
| Coldwellite | 9.90 | |
| Cooperite | 4.00 / 5.00 | 9.50 |
| Froodite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 12.50 |
| Genkinite | 5.50 / 6.00 | 8.83 |
| Hexatestibiopanickelite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 8.94 |
| Hollingworthite | 6.00 / 6.50 | 7.91 |
| Isoferroplatinum | 5.00 / 5.00 | 16.50 |
| Isomertieite | 5.50 / 5.50 | 10.33 |
| Jagüéite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 8.01 |
| Kalungaite | 7.59 | |
| Keithconnite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 10.00 |
| Kojonenite | ||
| Kotulskite | 4.00 / 4.50 | 8.26 |
| Laflammeite | 3.50 / 3.50 | |
| Lisiguangite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 7.42 |
| Lukkulaisvaaraite | 4.00 | |
| Majakite | 6.00 / 6.00 | 9.33 |
| Malyshevite | ||
| Menshikovite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 10.65 |
| Merenskyite | 2.00 / 3.00 | |
| Mertieite-I | 5.50 / 5.50 | 10.60 |
| Mertieite-II | 6.00 / 6.00 | 11.29 |
| Michenerite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 9.50 |
| Miessiite | 2.00 / 2.50 | 10.94 |
| Milotaite | 4.50 / 4.50 | 7.95 |
| Moncheite | 2.00 / 3.00 | 10.00 |
| Naldrettite | 4.00 / 5.00 | |
| Nielsenite | ||
| Norilskite | 4.00 / 4.00 | |
| Oosterboschite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 8.48 |
| Oulankaite | 3.50 / 4.00 | 10.27 |
| Padmaite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 9.00 |
| Palarstanide | 5.00 / 5.00 | 10.00 |
| Palladinite | ||
| Palladium | 4.50 / 5.00 | 11.30 |
| Palladoarsenide | 5.00 / 5.00 | 10.42 |
| Palladobismutharsenide | 5.00 / 5.00 | 10.86 |
| Palladodymite | ||
| Palladosilicide | 9.56 | |
| Palladseite | 4.50 / 5.00 | 8.30 |
| Paolovite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 11.32 |
| Pašavaite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 9.90 |
| Plumbopalladinite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 12.40 |
| Polarite | 3.50 / 4.00 | 12.51 |
| Potarite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 14.88 |
| Rhodarsenide | 4.00 / 5.00 | 11.27 |
| Rustenburgite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 15.00 |
| Skaergaardite | 4.00 / 5.00 | 10.64 |
| Sobolevskite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 11.88 |
| Sopcheite | 3.50 / 3.50 | |
| Stannopalladinite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 10.20 |
| Stibiopalladinite | 4.00 / 5.00 | 9.50 |
| Stillwaterite | 4.50 / 4.50 | 10.40 |
| Sudburyite | 4.50 / 4.50 | 9.00 |
| Taimyrite II | ||
| Taimyrite-I | 5.00 / 5.00 | |
| Tatyanaite | 3.50 / 4.00 | |
| Telargpalite | 2.00 / 2.50 | 7.38 |
| Telluropalladinite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 10.25 |
| Temagamite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 9.50 |
| Testìbiopalladite | 3.50 / 4.00 | 8.99 |
| Tischendorfite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 9.13 |
| Törnroosite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 11.21 |
| Ungavaite | 7.26 | |
| Urvantsevite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 9.66 |
| Vasilite | 5.00 / 5.50 | 8.79 |
| Vavrínite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 7.79 |
| Verbeekite | 5.50 / 5.50 | 7.21 |
| Vincentite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 6.82 |
| Vysotskite | 1.50 / 1.50 | 6.69 |
| Zvyagintsevite | 4.50 / 4.50 | 13.32 |
 mineraly.fr
mineraly.fr
 mineraly.co.uk
mineraly.co.uk
 mineraly.com.de
mineraly.com.de
 mineraly.it
mineraly.it
 mineraly.es
mineraly.es
 mineraly.nl
mineraly.nl
 mineraly.pt
mineraly.pt
 mineraly.se
mineraly.se