List of elements
»
Actinium
»
Aluminum
»
Antimony
»
Argon
»
Arsenic
»
astatine
»
Barium
»
Bismuth
»
bohrium
»
Boron
»
Bromine
»
Cadmium
»
Calcium
»
Carbon
»
Cerium
»
cesium
»
Chlorine
»
Chromium
»
Cobalt
»
Copper
»
Curium
»
dubnium
»
Erbium
»
Europium
»
fermium
»
Fluorine
»
francium
»
Gallium
»
Gold
»
Hafnium
»
hassium
»
Helium
»
holmium
»
Hydrogen
»
Indium
»
Iodine
»
Iridium
»
Iron
»
Krypton
»
Lead
»
Lithium
»
lutetium
»
Mercury
»
Neon
»
Nickel
»
Nihonium
»
Niobium
»
Nitrogen
»
nobelium
»
Osmium
»
Oxygen
»
Platinum
»
Polonium
»
Radium
»
Radon
»
Rhenium
»
rhodium
»
Rubidium
»
Samarium
»
scandium
»
Selenium
»
Silicon
»
Silver
»
Sodium
»
Sulfur
»
Tantalum
»
Terbium
»
Thallium
»
Thorium
»
Thulium
»
Tin
»
Titanium
»
Tungsten
»
Uranium
»
Vanadium
»
Xenon
»
Yttrium
»
Zinc
C - Carbon - OTHER NO METAL
Carbon is a chemical element essential to life and to the manufacture of products of all kinds. It is represented by the symbol C and is found in abundance in the environment as organic carbon (as in coal, hydrocarbons, etc.) and inorganic form (as carbon dioxide [CO2], carbon monoxide carbon [CO], etc.). It is a vital element of organized life on Earth.
carbon is colorless, odorless and combines with other elements to form organic and inorganic compounds. It is considered one of the three elements that play a major role in organic chemistry (along with hydrogen and oxygen). carbon bonds with itself and other elements to form molecules whose properties are determined by the type of bond between the carbon atoms.
carbon is a versatile element and the molecules it forms can have varying properties. The most important properties with carbon are electrical conductivity, thermal resistance and ability to absorb moisture. Products made from carbon are widely used in industry and in everyday life. The main carbon-based products are fuels, plastics, dyes, inks, steel, textiles, and chemicals for cosmetics and medicines.
carbon is also an important element for the production and storage of energy. carbon is used to generate energy in power plants and can be stored in the form of coal, natural gas and oil. Fossil fuels can be converted into energy from the carbon they contain. carbon can also be stored in the form of biomass (organic plant or animal matter), carbon dioxide or carbon-based chemicals.
carbon is colorless, odorless and combines with other elements to form organic and inorganic compounds. It is considered one of the three elements that play a major role in organic chemistry (along with hydrogen and oxygen). carbon bonds with itself and other elements to form molecules whose properties are determined by the type of bond between the carbon atoms.
carbon is a versatile element and the molecules it forms can have varying properties. The most important properties with carbon are electrical conductivity, thermal resistance and ability to absorb moisture. Products made from carbon are widely used in industry and in everyday life. The main carbon-based products are fuels, plastics, dyes, inks, steel, textiles, and chemicals for cosmetics and medicines.
carbon is also an important element for the production and storage of energy. carbon is used to generate energy in power plants and can be stored in the form of coal, natural gas and oil. Fossil fuels can be converted into energy from the carbon they contain. carbon can also be stored in the form of biomass (organic plant or animal matter), carbon dioxide or carbon-based chemicals.
Synthetic
Radioactive
Liquid
Gaseous
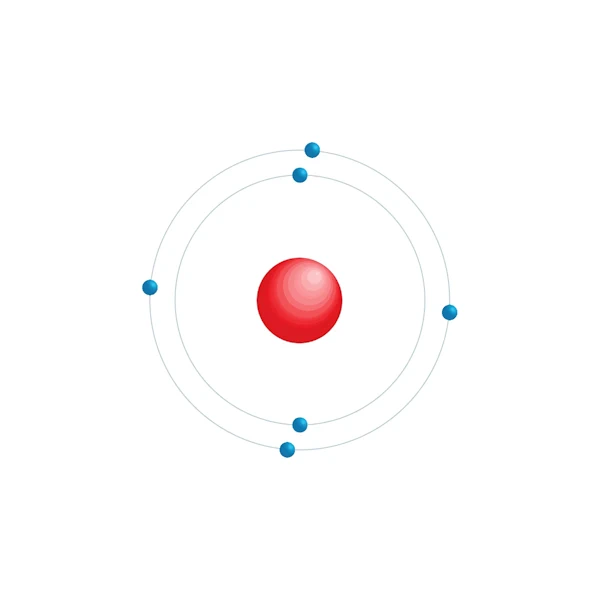
Electronic configuration diagram
| Name | Carbon |
| Number | 6 |
| Atomic | 12.0112 |
| Symbol | C |
| Fusion | 3550 |
| Boiling | 4827 |
| Density | 2.267 |
| Period | 2 |
| Group | 14 |
| Discovery | 0 Prehistoric |
| Abundance | 200 |
| Radius | 0.91 |
| Electronegativity | 2.55 |
| Ionization | 11.2603 |
| Number of isotopes | 7 |
| Electronic configuration | [He] 2s2 2p2 |
| Oxidation states | -4,-3,-2,-1,1,2,3,4 |
| Electron by energy level | 2,4 |
| Mineral | Hardness | Density |
| Abelsonite | 2.00 / 2.50 | 1.45 |
| Abenakiite-(Ce) | 4.00 / 4.00 | 3.21 |
| Acetamide | 1.00 / 1.50 | 1.17 |
| Adamsite-(Y) | 3.00 / 3.00 | |
| Aerinite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 2.48 |
| Afghanite | 5.50 / 6.00 | 2.55 |
| Agaite | 6.99 | |
| Agricolaite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 3.53 |
| Albrechtschraufite | 2.00 / 3.00 | 2.60 |
| Alexkhomyakovite | ||
| Alloriite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.35 |
| Alstonite | 4.00 / 4.50 | 3.69 |
| Alumohydrocalcite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 2.23 |
| Amber | 2.00 / 2.50 | 1.10 |
| Ammonite | 6.00 / 7.00 | 3.20 |
| Ancylite-(Ce) | 4.50 / 4.50 | 3.90 |
| Ancylite-(La) | 4.00 / 4.50 | 3.88 |
| Andersonite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 2.79 |
| Ankerite | 3.50 / 4.00 | 3.00 |
| Antipinite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 2.55 |
| Aragonite | 3.50 / 4.00 | 2.93 |
| Arisite-(Ce) | ||
| Arisite-(La) | 3.00 / 3.50 | 4.07 |
| Armangite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 4.43 |
| Artinite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 2.00 |
| Ashburtonite | 4.69 | |
| Ashcroftine-(Y) | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.61 |
| Astrocyanite-(Ce) | 2.00 / 3.00 | 3.80 |
| Aurichalcite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 3.64 |
| Azurite | 3.50 / 4.00 | 3.77 |
| Balliranoite | ||
| Barbertonite | 1.50 / 2.00 | 2.10 |
| Barentsite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 2.56 |
| Barringtonite | 2.83 | |
| Barstowite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 5.50 |
| Barytocalcite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 3.64 |
| Bastnäsite-(Ce) | 4.00 / 5.00 | 4.95 |
| Bastnäsite-(La) | 4.00 / 5.00 | 4.95 |
| Bastnäsite-(Nd) | 4.00 / 4.50 | 5.23 |
| Bastnäsite-(Y) | 4.00 / 4.50 | 4.90 |
| Bayleyite | 2.05 | |
| Baylissite | 2.00 | |
| Benstonite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 3.60 |
| Beyerite | 2.00 / 3.00 | 6.56 |
| Bijvoetite-(Y) | 2.00 / 2.00 | 3.90 |
| Biraite-(Ce) | 5.00 / 5.00 | 4.76 |
| Birunite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 2.36 |
| Bismutite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 7.00 |
| Blatonite | 2.00 / 3.00 | 3.99 |
| Bonshtedtite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 2.95 |
| Borcarite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 2.77 |
| Bosoite | ||
| Bradleyite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 2.73 |
| Braunerite | ||
| Brenkite | 3.10 | |
| Brianyoungite | 2.00 / 2.50 | 3.93 |
| Britvinite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 5.51 |
| Brugnatellite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 2.14 |
| Burbankite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 3.50 |
| Burkeite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 2.57 |
| Bussenite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 3.63 |
| Bütschliite | 2.00 | |
| Calcioancylite-(Ce) | 4.00 / 4.50 | |
| Calcioancylite-(Nd) | 4.00 / 4.50 | |
| Calcioburbankite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 3.45 |
| Calcite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 2.71 |
| Calclacite | 1.00 | |
| Caledonite | 2.50 / 3.00 | 5.70 |
| Calkinsite-(Ce) | 2.50 / 2.50 | 3.27 |
| Callaghanite | 3.00 / 3.50 | 2.71 |
| Camérolaite | 3.10 | |
| Canavesite | 1.80 | |
| Cancrinite | 6.00 / 6.00 | 2.40 |
| Cancrisilite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.40 |
| Caoxite | 2.00 / 2.50 | 1.85 |
| Carboborite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 2.12 |
| Carbobystrite | 6.00 / 6.00 | 2.37 |
| Carbocernaite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 3.53 |
| Carbokentbrooksite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 3.14 |
| Carbonate-fluorapatite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 3.12 |
| Carbonate-hydroxylapatite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 3.00 |
| Carbonatecyanotrichite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 2.65 |
| Carborandite | ||
| Caresite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 2.57 |
| Carletonite | 4.00 / 4.50 | 2.45 |
| Carpathite | 1.50 / 1.50 | 1.29 |
| Carraraite | ||
| Carrboydite | 2.50 | |
| Caysichite-(Y) | 4.50 / 4.50 | 3.03 |
| Cebaite-(Ce) | 4.50 / 5.00 | 4.81 |
| Cebaite-(Nd) | 4.50 / 5.00 | 4.80 |
| Cejkaite | 3.67 | |
| Cerussite | 3.00 / 3.50 | 6.50 |
| Chalconatronite | 1.00 / 2.00 | 2.27 |
| Chanabayaite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 1.46 |
| Chaoite | 1.00 / 2.00 | 3.33 |
| Charmarite | ||
| Chibaite | 6.50 / 7.00 | 1.93 |
| Chlorartinite | 1.87 |
 mineraly.fr
mineraly.fr
 mineraly.co.uk
mineraly.co.uk
 mineraly.com.de
mineraly.com.de
 mineraly.it
mineraly.it
 mineraly.es
mineraly.es
 mineraly.nl
mineraly.nl
 mineraly.pt
mineraly.pt
 mineraly.se
mineraly.se