List of elements
»
Actinium
»
Aluminum
»
Antimony
»
Argon
»
Arsenic
»
astatine
»
Barium
»
Bismuth
»
bohrium
»
Boron
»
Bromine
»
Cadmium
»
Calcium
»
Carbon
»
Cerium
»
cesium
»
Chlorine
»
Chromium
»
Cobalt
»
Copper
»
Curium
»
dubnium
»
Erbium
»
Europium
»
fermium
»
Fluorine
»
francium
»
Gallium
»
Gold
»
Hafnium
»
hassium
»
Helium
»
holmium
»
Hydrogen
»
Indium
»
Iodine
»
Iridium
»
Iron
»
Krypton
»
Lead
»
Lithium
»
lutetium
»
Mercury
»
Neon
»
Nickel
»
Nihonium
»
Niobium
»
Nitrogen
»
nobelium
»
Osmium
»
Oxygen
»
Platinum
»
Polonium
»
Radium
»
Radon
»
Rhenium
»
rhodium
»
Rubidium
»
Samarium
»
scandium
»
Selenium
»
Silicon
»
Silver
»
Sodium
»
Sulfur
»
Tantalum
»
Terbium
»
Thallium
»
Thorium
»
Thulium
»
Tin
»
Titanium
»
Tungsten
»
Uranium
»
Vanadium
»
Xenon
»
Yttrium
»
Zinc
Xe - Xenon - NO NOBLE GAS METAL
Xenon is a natural chemical element, atomic number 54, symbol Xe and atomic mass 131.293. It is an odorless and colorless noble gas that is found in the Earth's atmosphere in very low concentrations. It is chemically inert and stable in its normal state.
xenon has a molar mass of 131.3 g/mol and a vapor pressure of 16.6 kPa at 25°C. It is heavier than air and at atmospheric pressure its boiling point is -111.8°C. It has a melting point of -108.1°C and a relatively low density of 4.94 g/l at 25°C.
xenon is widely used for its cooling and luminous properties. It is used to produce fluorescent lights and for medical applications such as x-ray scanners or xenon lasers. It is also used to inflate tires, to produce plasma beams and to make vacuum pumps. xenon is also used in the automotive industry for headlights and to fill new vehicle fuel tanks. In addition, xenon is used in scientific research to study various physical and chemical effects, such as gas diffusion and radiation absorption.
xenon has a molar mass of 131.3 g/mol and a vapor pressure of 16.6 kPa at 25°C. It is heavier than air and at atmospheric pressure its boiling point is -111.8°C. It has a melting point of -108.1°C and a relatively low density of 4.94 g/l at 25°C.
xenon is widely used for its cooling and luminous properties. It is used to produce fluorescent lights and for medical applications such as x-ray scanners or xenon lasers. It is also used to inflate tires, to produce plasma beams and to make vacuum pumps. xenon is also used in the automotive industry for headlights and to fill new vehicle fuel tanks. In addition, xenon is used in scientific research to study various physical and chemical effects, such as gas diffusion and radiation absorption.
Synthetic
Radioactive
Liquid
Gaseous
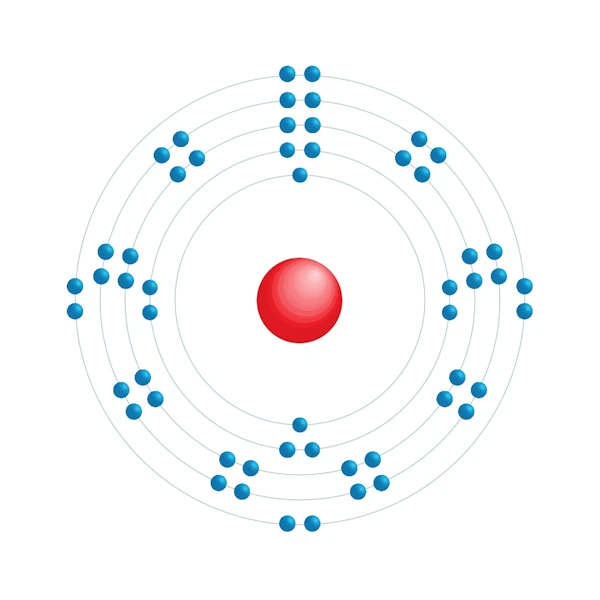
Electronic configuration diagram
| Name | Xenon |
| Number | 54 |
| Atomic | 131.293 |
| Symbol | Xe |
| Fusion | -111.9 |
| Boiling | -107 |
| Density | 0.005887 |
| Period | 5 |
| Group | 18 |
| Discovery | 1898 Ramsay and Travers |
| Abundance | 0.001 |
| Radius | 1.2 |
| Electronegativity | 0 |
| Ionization | 12.1298 |
| Number of isotopes | 31 |
| Electronic configuration | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p6 |
| Oxidation states | 2,4,6,8 |
| Electron by energy level | 2,8,18,18,8 |
 mineraly.fr
mineraly.fr
 mineraly.co.uk
mineraly.co.uk
 mineraly.com.de
mineraly.com.de
 mineraly.it
mineraly.it
 mineraly.es
mineraly.es
 mineraly.nl
mineraly.nl
 mineraly.pt
mineraly.pt
 mineraly.se
mineraly.se