List of elements
»
Actinium
»
Aluminum
»
Antimony
»
Argon
»
Arsenic
»
astatine
»
Barium
»
Bismuth
»
bohrium
»
Boron
»
Bromine
»
Cadmium
»
Calcium
»
Carbon
»
Cerium
»
cesium
»
Chlorine
»
Chromium
»
Cobalt
»
Copper
»
Curium
»
dubnium
»
Erbium
»
Europium
»
fermium
»
Fluorine
»
francium
»
Gallium
»
Gold
»
Hafnium
»
hassium
»
Helium
»
holmium
»
Hydrogen
»
Indium
»
Iodine
»
Iridium
»
Iron
»
Krypton
»
Lead
»
Lithium
»
lutetium
»
Mercury
»
Neon
»
Nickel
»
Nihonium
»
Niobium
»
Nitrogen
»
nobelium
»
Osmium
»
Oxygen
»
Platinum
»
Polonium
»
Radium
»
Radon
»
Rhenium
»
rhodium
»
Rubidium
»
Samarium
»
scandium
»
Selenium
»
Silicon
»
Silver
»
Sodium
»
Sulfur
»
Tantalum
»
Terbium
»
Thallium
»
Thorium
»
Thulium
»
Tin
»
Titanium
»
Tungsten
»
Uranium
»
Vanadium
»
Xenon
»
Yttrium
»
Zinc
mineralogy
elements
Cd Cadmium
Cd - Cadmium - POOR METAL
Cadmium is a metallic chemical element, making up atomic number 48 of the Periodic Table of Elements. It is part of the transition metal family of the periodic table. Its chemical symbol is Cd.
cadmium has a shiny metallic, pale silvery gray appearance and is relatively soft. Its density is 8.65 g/cm3 and its melting temperature is 321°C.
cadmium is a very reactive element and easily reacts with oxygen to form oxides. It also exchanges with salts such as sulfate and phosphate to form salts such as sulfide and cadmium phosphate.
cadmium is a toxic element, and in high doses it can be harmful to humans. However, it is also used for some industrial and medical uses. In industry, it is mainly used in the production of batteries, coatings and plastics. It is also used in the manufacture of stainless steel, fiber optics and electronic components. cadmium is also used to treat certain cancers and other diseases.
Since cadmium is a very reactive metal, it is also important that people who work with this metal take the necessary steps to protect themselves from exposure. It is also important to ensure that cadmium is not released into the environment, as it can accumulate in soil and water bodies and become a source of pollution.
cadmium has a shiny metallic, pale silvery gray appearance and is relatively soft. Its density is 8.65 g/cm3 and its melting temperature is 321°C.
cadmium is a very reactive element and easily reacts with oxygen to form oxides. It also exchanges with salts such as sulfate and phosphate to form salts such as sulfide and cadmium phosphate.
cadmium is a toxic element, and in high doses it can be harmful to humans. However, it is also used for some industrial and medical uses. In industry, it is mainly used in the production of batteries, coatings and plastics. It is also used in the manufacture of stainless steel, fiber optics and electronic components. cadmium is also used to treat certain cancers and other diseases.
Since cadmium is a very reactive metal, it is also important that people who work with this metal take the necessary steps to protect themselves from exposure. It is also important to ensure that cadmium is not released into the environment, as it can accumulate in soil and water bodies and become a source of pollution.
Synthetic
Radioactive
Liquid
Gaseous
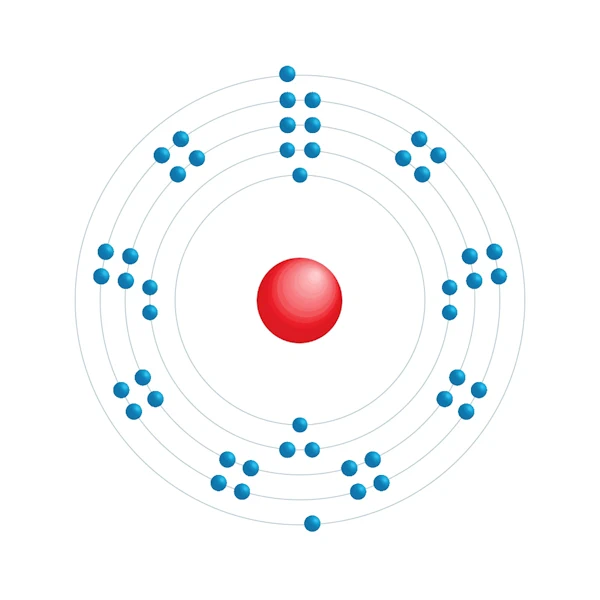
Electronic configuration diagram
| Name | Cadmium |
| Number | 48 |
| Atomic | 112.414 |
| Symbol | Cd |
| Fusion | 321 |
| Boiling | 765 |
| Density | 8.69 |
| Period | 5 |
| Group | 12 |
| Discovery | 1817 Stromeyer |
| Abundance | 0.159 |
| Radius | 1.7 |
| Electronegativity | 1.69 |
| Ionization | 8.9938 |
| Number of isotopes | 22 |
| Electronic configuration | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 |
| Oxidation states | 2 |
| Electron by energy level | 2,8,18,18,2 |
| Mineral | Hardness | Density |
| Aldridgeite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 3.33 |
| Andyrobertsite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 4.01 |
| Barquillite | 4.00 / 4.50 | 4.53 |
| Birchite | 3.50 / 4.00 | 3.61 |
| Burnsite | 1.00 / 1.50 | |
| Cadmium | 1.00 / 2.00 | 8.60 |
| Cadmoindite | ||
| Cadmoselite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 5.66 |
| Cadmoxite | ||
| Cernýite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 4.78 |
| Drobecite | ||
| Edwardsite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 3.53 |
| Goldquarryite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 2.78 |
| Greenockite | 3.50 / 4.00 | 3.98 |
| Hawleyite | 2.50 / 3.00 | 4.87 |
| Jonassonite | 2.50 / 3.00 | |
| Keyite | 3.50 / 4.00 | 4.95 |
| Kudriavite | 6.58 | |
| Kupcíkite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 6.42 |
| Lazaridisite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 3.01 |
| Monteponite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 8.10 |
| Niedermayrite | 3.36 | |
| Nyholmite | 3.00 / 3.50 | 4.23 |
| Otavite | 3.50 / 4.00 | 5.03 |
| Quadratite | 3.00 / 3.00 | |
| Ramdohrite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 5.33 |
| Shadlunite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 4.00 |
| Tazieffite | 6.07 | |
| Vanackerite | 7.28 | |
| Voudourisite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 3.69 |
 mineraly.fr
mineraly.fr
 mineraly.co.uk
mineraly.co.uk
 mineraly.com.de
mineraly.com.de
 mineraly.it
mineraly.it
 mineraly.es
mineraly.es
 mineraly.nl
mineraly.nl
 mineraly.pt
mineraly.pt
 mineraly.se
mineraly.se