List of elements
»
Actinium
»
Aluminum
»
Antimony
»
Argon
»
Arsenic
»
astatine
»
Barium
»
Bismuth
»
bohrium
»
Boron
»
Bromine
»
Cadmium
»
Calcium
»
Carbon
»
Cerium
»
cesium
»
Chlorine
»
Chromium
»
Cobalt
»
Copper
»
Curium
»
dubnium
»
Erbium
»
Europium
»
fermium
»
Fluorine
»
francium
»
Gallium
»
Gold
»
Hafnium
»
hassium
»
Helium
»
holmium
»
Hydrogen
»
Indium
»
Iodine
»
Iridium
»
Iron
»
Krypton
»
Lead
»
Lithium
»
lutetium
»
Mercury
»
Neon
»
Nickel
»
Nihonium
»
Niobium
»
Nitrogen
»
nobelium
»
Osmium
»
Oxygen
»
Platinum
»
Polonium
»
Radium
»
Radon
»
Rhenium
»
rhodium
»
Rubidium
»
Samarium
»
scandium
»
Selenium
»
Silicon
»
Silver
»
Sodium
»
Sulfur
»
Tantalum
»
Terbium
»
Thallium
»
Thorium
»
Thulium
»
Tin
»
Titanium
»
Tungsten
»
Uranium
»
Vanadium
»
Xenon
»
Yttrium
»
Zinc
He - Helium - NO NOBLE GAS METAL
Helium is the second lightest chemical element on the periodic scale of the elements, and the most abundant in the universe. Its atomic number is 2, and its atomic mass is 4,003 amu (Atomic Mass Units).
helium is an inert element, that is, it does not react to most other chemical elements. It does not combine with other elements, and is stable at room temperature and pressure, except for extreme conditions. It has no odor or taste, and is transparent to visible light.
helium is very light and has a melting point of -452.2°F (-268.9°C). Its boiling point is the highest of all the elements, at -452.1°F (-268.9°C). It is also very unreactive and does not combine with other elements, which makes it an excellent thermal insulator and an inert gas to protect other flammable gases.
helium is used in many industries, including cooling, beacon systems, and medicine. It is also used to fill balloons and hot air dirigibles. It is also used in the manufacture of fiber optics, for lighting and personal safety. Finally, it is used for filling the exhaust gases of combustion engines, in order to reduce carbon emissions.
helium is an inert element, that is, it does not react to most other chemical elements. It does not combine with other elements, and is stable at room temperature and pressure, except for extreme conditions. It has no odor or taste, and is transparent to visible light.
helium is very light and has a melting point of -452.2°F (-268.9°C). Its boiling point is the highest of all the elements, at -452.1°F (-268.9°C). It is also very unreactive and does not combine with other elements, which makes it an excellent thermal insulator and an inert gas to protect other flammable gases.
helium is used in many industries, including cooling, beacon systems, and medicine. It is also used to fill balloons and hot air dirigibles. It is also used in the manufacture of fiber optics, for lighting and personal safety. Finally, it is used for filling the exhaust gases of combustion engines, in order to reduce carbon emissions.
Synthetic
Radioactive
Liquid
Gaseous
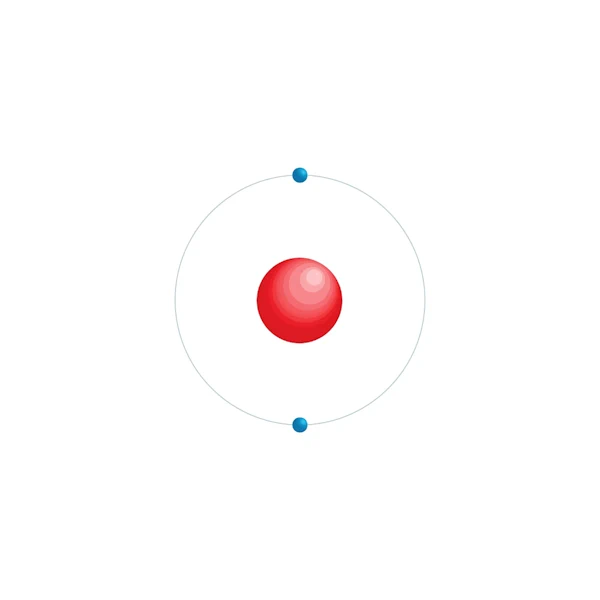
Electronic configuration diagram
| Name | Helium |
| Number | 2 |
| Atomic | 4.002602 |
| Symbol | He |
| Fusion | -272.2 |
| Boiling | -268.9 |
| Density | 0.0001785 |
| Period | 1 |
| Group | 18 |
| Discovery | 1868 Janssen |
| Abundance | 0.008 |
| Radius | 0.49 |
| Electronegativity | 0 |
| Ionization | 24.5874 |
| Number of isotopes | 5 |
| Electronic configuration | 1s2 |
| Oxidation states | 0 |
| Electron by energy level | 2 |
 mineraly.fr
mineraly.fr
 mineraly.co.uk
mineraly.co.uk
 mineraly.com.de
mineraly.com.de
 mineraly.it
mineraly.it
 mineraly.es
mineraly.es
 mineraly.nl
mineraly.nl
 mineraly.pt
mineraly.pt
 mineraly.se
mineraly.se