List of elements
»
Actinium
»
Aluminum
»
Antimony
»
Argon
»
Arsenic
»
astatine
»
Barium
»
Bismuth
»
bohrium
»
Boron
»
Bromine
»
Cadmium
»
Calcium
»
Carbon
»
Cerium
»
cesium
»
Chlorine
»
Chromium
»
Cobalt
»
Copper
»
Curium
»
dubnium
»
Erbium
»
Europium
»
fermium
»
Fluorine
»
francium
»
Gallium
»
Gold
»
Hafnium
»
hassium
»
Helium
»
holmium
»
Hydrogen
»
Indium
»
Iodine
»
Iridium
»
Iron
»
Krypton
»
Lead
»
Lithium
»
lutetium
»
Mercury
»
Neon
»
Nickel
»
Nihonium
»
Niobium
»
Nitrogen
»
nobelium
»
Osmium
»
Oxygen
»
Platinum
»
Polonium
»
Radium
»
Radon
»
Rhenium
»
rhodium
»
Rubidium
»
Samarium
»
scandium
»
Selenium
»
Silicon
»
Silver
»
Sodium
»
Sulfur
»
Tantalum
»
Terbium
»
Thallium
»
Thorium
»
Thulium
»
Tin
»
Titanium
»
Tungsten
»
Uranium
»
Vanadium
»
Xenon
»
Yttrium
»
Zinc
mineralogy
elements
Ge Germanium
Ge - Germanium - METALLOIDS
Germanium is a chemical element whose symbol is Ge and which has the atomic number 32 on the periodic table. It is a semiconductor metal that is in the silicon family. germanium is a shiny silver-grey metal that breaks into fine flakes.
germanium is an unstable metallic element that dissolves in basic solutions and forms oxides. It is quite reactive but not enough to decompose spontaneously. It is very strong and its melting point is around 937°C. It is generally soluble in mineral leaches but not in acid solutions.
germanium is a semiconductor that is known for its great ability to transmit electronic signals. It is used to make transistors and diodes which are an important part of electronic circuits. It is the main component of alloys specially designed for use on junctions which are interfaces between different electronic systems.
germanium is used in the optical industry for applications such as the manufacture of lenses and mirrors. It is also used for the manufacture of optical fibers and optical instruments. It is used in the manufacture of electronic components and circuits, including semiconductor light-emitting diodes and transistors.
germanium is an unstable metallic element that dissolves in basic solutions and forms oxides. It is quite reactive but not enough to decompose spontaneously. It is very strong and its melting point is around 937°C. It is generally soluble in mineral leaches but not in acid solutions.
germanium is a semiconductor that is known for its great ability to transmit electronic signals. It is used to make transistors and diodes which are an important part of electronic circuits. It is the main component of alloys specially designed for use on junctions which are interfaces between different electronic systems.
germanium is used in the optical industry for applications such as the manufacture of lenses and mirrors. It is also used for the manufacture of optical fibers and optical instruments. It is used in the manufacture of electronic components and circuits, including semiconductor light-emitting diodes and transistors.
Synthetic
Radioactive
Liquid
Gaseous
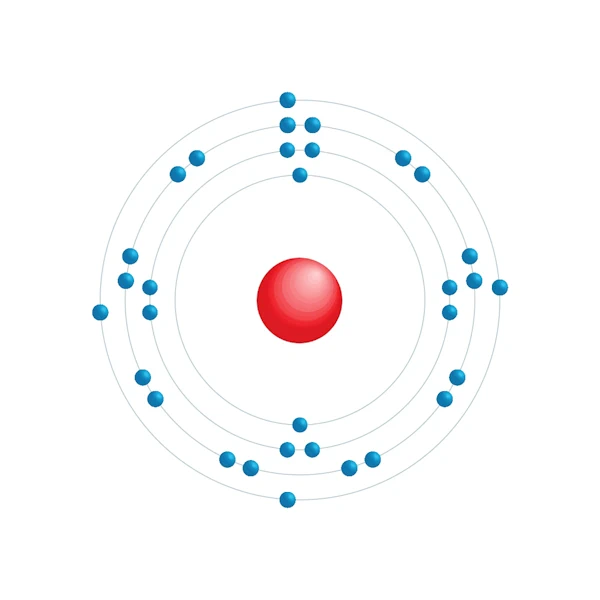
Electronic configuration diagram
| Name | Germanium |
| Number | 32 |
| Atomic | 72.63 |
| Symbol | Ge |
| Fusion | 937.4 |
| Boiling | 2830 |
| Density | 5.323 |
| Period | 4 |
| Group | 14 |
| Discovery | 1886 Winkler |
| Abundance | 1.5 |
| Radius | 1.5 |
| Electronegativity | 2.01 |
| Ionization | 7.8994 |
| Number of isotopes | 17 |
| Electronic configuration | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p2 |
| Oxidation states | -4,1,2,3,4 |
| Electron by energy level | 2,8,18,4 |
| Mineral | Hardness | Density |
| Alburnite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 7.83 |
| Argutite | 6.00 / 7.00 | |
| Argyrodite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 6.10 |
| Barquillite | 4.00 / 4.50 | 4.53 |
| Bartelkeite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 4.97 |
| Briartite | 3.50 / 4.00 | 4.50 |
| Brunogeierite | 4.50 / 4.50 | 5.51 |
| Cadmoindite | ||
| Calvertite | 4.00 / 5.00 | 5.24 |
| Carboirite | 6.00 / 6.00 | 3.00 |
| Carraraite | ||
| Catamarcaite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 4.89 |
| Colusite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 4.20 |
| Eyselite | 3.64 | |
| Fleischerite | 2.50 / 3.00 | 4.20 |
| Galloplumbogummite | 4.62 | |
| Germanite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 4.40 |
| Germanocolusite | 4.50 / 5.00 | 4.00 |
| Itoite | 6.67 | |
| Krieselite | 5.50 / 6.50 | 4.07 |
| Maikainite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 4.45 |
| Mathewrogersite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 4.70 |
| Morozeviczite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 6.62 |
| Nuwaite | ||
| Otjisumeite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 5.00 |
| Ovamboite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 4.74 |
| Polkovicite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 6.62 |
| Putzite | 3.00 / 3.50 | 5.79 |
| Renierite | 4.00 / 5.00 | 4.38 |
| Schaurteite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 2.65 |
| Stottite | 4.50 / 4.50 | 3.60 |
| Tsumgallite | 1.50 / 2.50 | 5.08 |
| Zincobriartite |
 mineraly.fr
mineraly.fr
 mineraly.co.uk
mineraly.co.uk
 mineraly.com.de
mineraly.com.de
 mineraly.it
mineraly.it
 mineraly.es
mineraly.es
 mineraly.nl
mineraly.nl
 mineraly.pt
mineraly.pt
 mineraly.se
mineraly.se