List of elements
»
Actinium
»
Aluminum
»
Antimony
»
Argon
»
Arsenic
»
astatine
»
Barium
»
Bismuth
»
bohrium
»
Boron
»
Bromine
»
Cadmium
»
Calcium
»
Carbon
»
Cerium
»
cesium
»
Chlorine
»
Chromium
»
Cobalt
»
Copper
»
Curium
»
dubnium
»
Erbium
»
Europium
»
fermium
»
Fluorine
»
francium
»
Gallium
»
Gold
»
Hafnium
»
hassium
»
Helium
»
holmium
»
Hydrogen
»
Indium
»
Iodine
»
Iridium
»
Iron
»
Krypton
»
Lead
»
Lithium
»
lutetium
»
Mercury
»
Neon
»
Nickel
»
Nihonium
»
Niobium
»
Nitrogen
»
nobelium
»
Osmium
»
Oxygen
»
Platinum
»
Polonium
»
Radium
»
Radon
»
Rhenium
»
rhodium
»
Rubidium
»
Samarium
»
scandium
»
Selenium
»
Silicon
»
Silver
»
Sodium
»
Sulfur
»
Tantalum
»
Terbium
»
Thallium
»
Thorium
»
Thulium
»
Tin
»
Titanium
»
Tungsten
»
Uranium
»
Vanadium
»
Xenon
»
Yttrium
»
Zinc
mineralogy
elements
Ru Ruthenium
Ru - Ruthenium - TRANSITION METAL
Ruthenium is a metallic chemical element with atomic number 44 and chemical symbol Ru. ruthenium is the 58th most abundant element in the earth's crust, making it a relatively rare element. It is one of the transition metals and is the newest member of the platinum family.
ruthenium is in solid form at room temperature. It is hard and brittle, bordering on white, and usually forms as a powder. It is slightly heavier than platinum, but slightly lighter than iridium.
ruthenium has several remarkable properties. It is an excellent catalyst and its chemical properties are similar to those of other transition metals. It is very resistant to acids, but is vulnerable to bleach and hydrogen peroxide. ruthenium is very refractory and can withstand extreme temperatures up to 1700°C.
ruthenium was first isolated in 1844 by Karl Klaus, a Russian chemist. Since then, it has been widely used for industrial purposes. This element is widely used in the manufacture of catalysts and internal combustion engines, as well as in the manufacture of metal wires, rods and other metal products. It is also used to make alloys for making metal parts that need to withstand high temperatures.
ruthenium is also used in medicine, especially for the manufacture of dental prostheses, crowns and bridges. It is also used for the treatment of heart disease and to treat certain cancers.
Finally, ruthenium is also used in the manufacture of jewelry and decorative objects, because it is very difficult to corrode and it is resistant to light, heat and chemicals.
ruthenium is in solid form at room temperature. It is hard and brittle, bordering on white, and usually forms as a powder. It is slightly heavier than platinum, but slightly lighter than iridium.
ruthenium has several remarkable properties. It is an excellent catalyst and its chemical properties are similar to those of other transition metals. It is very resistant to acids, but is vulnerable to bleach and hydrogen peroxide. ruthenium is very refractory and can withstand extreme temperatures up to 1700°C.
ruthenium was first isolated in 1844 by Karl Klaus, a Russian chemist. Since then, it has been widely used for industrial purposes. This element is widely used in the manufacture of catalysts and internal combustion engines, as well as in the manufacture of metal wires, rods and other metal products. It is also used to make alloys for making metal parts that need to withstand high temperatures.
ruthenium is also used in medicine, especially for the manufacture of dental prostheses, crowns and bridges. It is also used for the treatment of heart disease and to treat certain cancers.
Finally, ruthenium is also used in the manufacture of jewelry and decorative objects, because it is very difficult to corrode and it is resistant to light, heat and chemicals.
Synthetic
Radioactive
Liquid
Gaseous
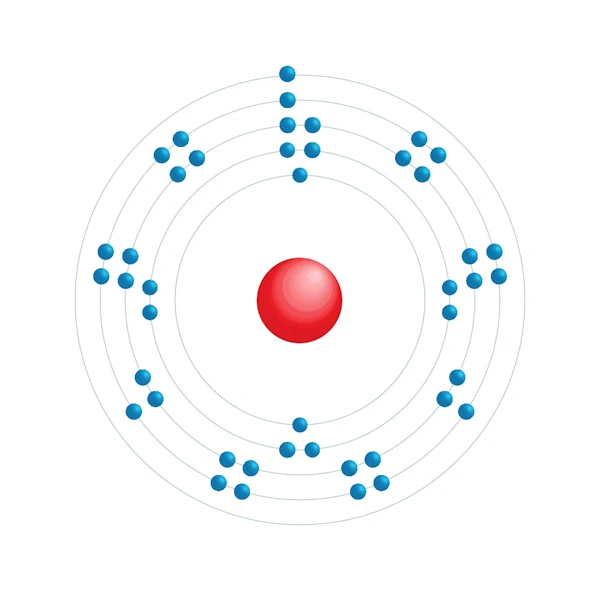
Electronic configuration diagram
| Name | Ruthenium |
| Number | 44 |
| Atomic | 101.07 |
| Symbol | Ru |
| Fusion | 2310 |
| Boiling | 3900 |
| Density | 12.37 |
| Period | 5 |
| Group | 8 |
| Discovery | 1844 Klaus |
| Abundance | 0.001 |
| Radius | 1.9 |
| Electronegativity | 2.2 |
| Ionization | 7.3605 |
| Number of isotopes | 16 |
| Electronic configuration | [Kr] 4d7 5s1 |
| Oxidation states | -2,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8 |
| Electron by energy level | 2,8,18,15,1 |
| Mineral | Hardness | Density |
| Anduoite | 7.00 / 7.00 | 8.00 |
| Hexaferrum | 6.00 / 7.00 | 10.69 |
| Hexamolybdenum | 11.90 | |
| Irarsite | 6.50 / 6.50 | 11.00 |
| Iridarsenite | 5.00 / 5.50 | 10.90 |
| Iridium | 6.00 / 7.00 | 22.60 |
| Laurite | 7.50 / 7.50 | 6.99 |
| Omeiite | 7.00 / 7.00 | 11.20 |
| Osarsite | 6.00 / 6.00 | 8.44 |
| Platarsite | 7.50 / 7.50 | 8.00 |
| Ruarsite | 6.00 / 7.00 | 7.00 |
| Ruthenarsenite | 6.00 / 6.50 | 10.00 |
| Rutheniridosmine | 6.00 / 7.00 | 21.00 |
| Ruthenium | 6.50 / 6.50 | 12.20 |
 mineraly.fr
mineraly.fr
 mineraly.co.uk
mineraly.co.uk
 mineraly.com.de
mineraly.com.de
 mineraly.it
mineraly.it
 mineraly.es
mineraly.es
 mineraly.nl
mineraly.nl
 mineraly.pt
mineraly.pt
 mineraly.se
mineraly.se