List of elements
»
Actinium
»
Aluminum
»
Antimony
»
Argon
»
Arsenic
»
astatine
»
Barium
»
Bismuth
»
bohrium
»
Boron
»
Bromine
»
Cadmium
»
Calcium
»
Carbon
»
Cerium
»
cesium
»
Chlorine
»
Chromium
»
Cobalt
»
Copper
»
Curium
»
dubnium
»
Erbium
»
Europium
»
fermium
»
Fluorine
»
francium
»
Gallium
»
Gold
»
Hafnium
»
hassium
»
Helium
»
holmium
»
Hydrogen
»
Indium
»
Iodine
»
Iridium
»
Iron
»
Krypton
»
Lead
»
Lithium
»
lutetium
»
Mercury
»
Neon
»
Nickel
»
Nihonium
»
Niobium
»
Nitrogen
»
nobelium
»
Osmium
»
Oxygen
»
Platinum
»
Polonium
»
Radium
»
Radon
»
Rhenium
»
rhodium
»
Rubidium
»
Samarium
»
scandium
»
Selenium
»
Silicon
»
Silver
»
Sodium
»
Sulfur
»
Tantalum
»
Terbium
»
Thallium
»
Thorium
»
Thulium
»
Tin
»
Titanium
»
Tungsten
»
Uranium
»
Vanadium
»
Xenon
»
Yttrium
»
Zinc
mineralogy
elements
Ga Gallium
Ga - Gallium - POOR METAL
Gallium is a metallic chemical element with the symbol Ga. It is the chemical element with atomic number 31 and atomic mass 69.723 g/mol. Its atomic binding energy is 624.5 kJ/mol.
gallium has a monatomic atom that makes covalent bonds with other atoms. It has a cubic structure with center faces. Its color is silver gray and it has a relatively low hardness.
gallium has a very low melting temperature (29.76°C) and a boiling temperature (2402°C). Its melting point is used for general purpose sensors because it reacts with heat and provides precise temperature control.
gallium is very soluble in organic materials and in strong acids, but it is insoluble in water. It also mixes easily with other elements to form alloys.
gallium is also used in the manufacture of LEDs (solid-state lighting) and in the computer industry for the production of processors, memory and integrated circuits.
gallium is also used in the medical industry for the production of radiopharmaceuticals and diagnostic products. It is also used in the production of cosmetics and pharmaceuticals. It is also used in the materials industry due to its thermal and chemical properties.
gallium has a monatomic atom that makes covalent bonds with other atoms. It has a cubic structure with center faces. Its color is silver gray and it has a relatively low hardness.
gallium has a very low melting temperature (29.76°C) and a boiling temperature (2402°C). Its melting point is used for general purpose sensors because it reacts with heat and provides precise temperature control.
gallium is very soluble in organic materials and in strong acids, but it is insoluble in water. It also mixes easily with other elements to form alloys.
gallium is also used in the manufacture of LEDs (solid-state lighting) and in the computer industry for the production of processors, memory and integrated circuits.
gallium is also used in the medical industry for the production of radiopharmaceuticals and diagnostic products. It is also used in the production of cosmetics and pharmaceuticals. It is also used in the materials industry due to its thermal and chemical properties.
Synthetic
Radioactive
Liquid
Gaseous
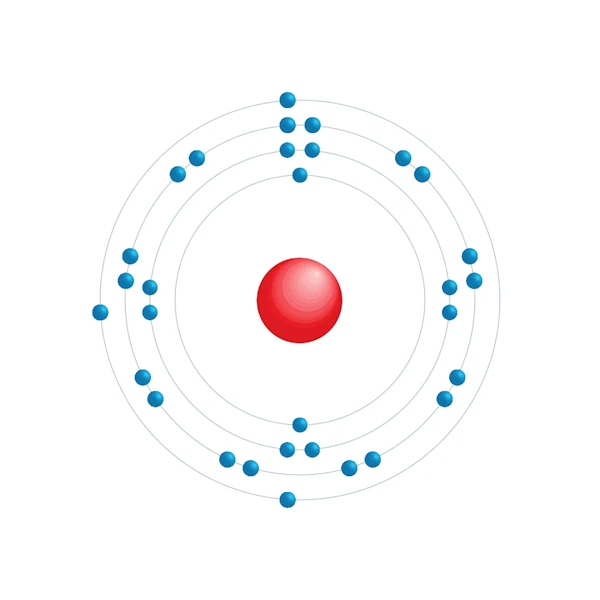
Electronic configuration diagram
| Name | Gallium |
| Number | 31 |
| Atomic | 69.723 |
| Symbol | Ga |
| Fusion | 29.8 |
| Boiling | 2403 |
| Density | 5.907 |
| Period | 4 |
| Group | 13 |
| Discovery | 1875 de Boisbaudran |
| Abundance | 19 |
| Radius | 1.8 |
| Electronegativity | 1.81 |
| Ionization | 5.9993 |
| Number of isotopes | 14 |
| Electronic configuration | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p1 |
| Oxidation states | 1,2,3 |
| Electron by energy level | 2,8,18,3 |
| Mineral | Hardness | Density |
| Calvertite | 4.00 / 5.00 | 5.24 |
| Dissakisite-(La) | 6.50 / 7.00 | 3.79 |
| Eyselite | 3.64 | |
| Ferrohögbomite-2N2S | 6.00 / 7.00 | |
| Gallite | 3.00 / 3.50 | 4.20 |
| Gallobeudantite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 4.58 |
| Galloplumbogummite | 4.62 | |
| Ishiharaite | ||
| Krieselite | 5.50 / 6.50 | 4.07 |
| Maikainite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 4.45 |
| Ovamboite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 4.74 |
| Söhngeite | 4.00 / 4.50 | 3.84 |
| Tsumgallite | 1.50 / 2.50 | 5.08 |
| Zincobriartite |
 mineraly.fr
mineraly.fr
 mineraly.co.uk
mineraly.co.uk
 mineraly.com.de
mineraly.com.de
 mineraly.it
mineraly.it
 mineraly.es
mineraly.es
 mineraly.nl
mineraly.nl
 mineraly.pt
mineraly.pt
 mineraly.se
mineraly.se