List of elements
»
Actinium
»
Aluminum
»
Antimony
»
Argon
»
Arsenic
»
astatine
»
Barium
»
Bismuth
»
bohrium
»
Boron
»
Bromine
»
Cadmium
»
Calcium
»
Carbon
»
Cerium
»
cesium
»
Chlorine
»
Chromium
»
Cobalt
»
Copper
»
Curium
»
dubnium
»
Erbium
»
Europium
»
fermium
»
Fluorine
»
francium
»
Gallium
»
Gold
»
Hafnium
»
hassium
»
Helium
»
holmium
»
Hydrogen
»
Indium
»
Iodine
»
Iridium
»
Iron
»
Krypton
»
Lead
»
Lithium
»
lutetium
»
Mercury
»
Neon
»
Nickel
»
Nihonium
»
Niobium
»
Nitrogen
»
nobelium
»
Osmium
»
Oxygen
»
Platinum
»
Polonium
»
Radium
»
Radon
»
Rhenium
»
rhodium
»
Rubidium
»
Samarium
»
scandium
»
Selenium
»
Silicon
»
Silver
»
Sodium
»
Sulfur
»
Tantalum
»
Terbium
»
Thallium
»
Thorium
»
Thulium
»
Tin
»
Titanium
»
Tungsten
»
Uranium
»
Vanadium
»
Xenon
»
Yttrium
»
Zinc
mineralogy
elements
Sr Strontium
Sr - Strontium - ALKALINE EARTH METAL
Strontium is a light metallic chemical element belonging to the alkaline-earth family. Its symbol is Sr and its atomic number is 38. It is one of the three elements of the strontium group, the second being barium and the third being calcium.
strontium is a soft and ductile metal. It has a delicate metallic white color and is very responsive. Its reactivity is close to that of calcium, with which it is very similar in its chemical properties. It is soluble in hydrochloric acid and dissolves with difficulty in basic solution. It reacts strongly with water and releases flammable gases.
The main chemical uses of strontium are in metal alloys for metal coating, welding, casting and casting. It is also used in explosives, luminescents and pigments. Alloys containing strontium are used as lubricants and for various mechanical applications.
strontium is also an important element in the nuclear industry. It is used in the manufacture of strontium-90 compounds, a radioactive isotope used to treat tumors. It is also a key source of neutrons in the operation of nuclear reactors.
In medicine, strontium has potential benefits and risks. Studies suggest that it can help strengthen bones and improve bone density. However, there is limited evidence that it may increase the risk of cancer, and health authorities closely monitor its consumption.
strontium is a soft and ductile metal. It has a delicate metallic white color and is very responsive. Its reactivity is close to that of calcium, with which it is very similar in its chemical properties. It is soluble in hydrochloric acid and dissolves with difficulty in basic solution. It reacts strongly with water and releases flammable gases.
The main chemical uses of strontium are in metal alloys for metal coating, welding, casting and casting. It is also used in explosives, luminescents and pigments. Alloys containing strontium are used as lubricants and for various mechanical applications.
strontium is also an important element in the nuclear industry. It is used in the manufacture of strontium-90 compounds, a radioactive isotope used to treat tumors. It is also a key source of neutrons in the operation of nuclear reactors.
In medicine, strontium has potential benefits and risks. Studies suggest that it can help strengthen bones and improve bone density. However, there is limited evidence that it may increase the risk of cancer, and health authorities closely monitor its consumption.
Synthetic
Radioactive
Liquid
Gaseous
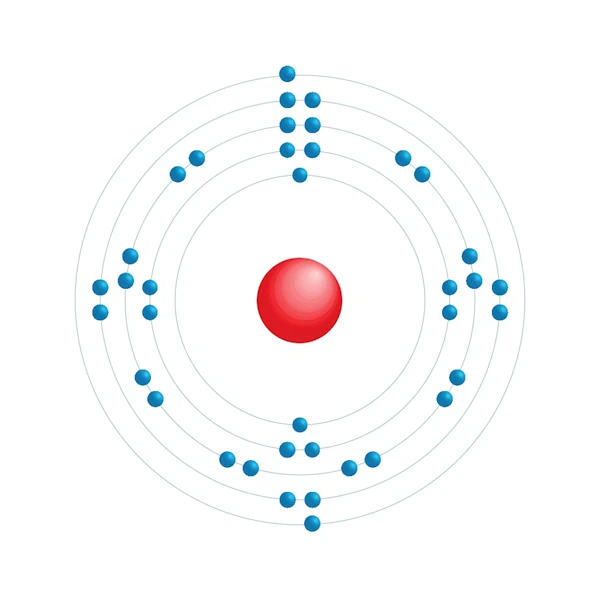
Electronic configuration diagram
| Name | Strontium |
| Number | 38 |
| Atomic | 87.62 |
| Symbol | Sr |
| Fusion | 769 |
| Boiling | 1384 |
| Density | 2.64 |
| Period | 5 |
| Group | 2 |
| Discovery | 1808 Davy |
| Abundance | 370 |
| Radius | 2.5 |
| Electronegativity | 0.95 |
| Ionization | 5.6949 |
| Number of isotopes | 18 |
| Electronic configuration | [Kr] 5s2 |
| Oxidation states | 2 |
| Electron by energy level | 2,8,18,8,2 |
| Mineral | Hardness | Density |
| Acuminite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 3.30 |
| Agrinierite | 5.62 | |
| Alsakharovite-Zn | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.90 |
| Ancylite-(Ce) | 4.50 / 4.50 | 3.90 |
| Ancylite-(La) | 4.00 / 4.50 | 3.88 |
| Andrianovite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 3.02 |
| Aqualite | 4.00 / 5.00 | 2.66 |
| Arrojadite-(BaFe) | 3.54 | |
| Arrojadite-(KNa) | ||
| Arrojadite-(SrFe) | ||
| Arsenocrandallite | 5.50 / 5.50 | 3.25 |
| Arsenoflorencite-(La) | 3.50 / 3.50 | 4.10 |
| Arsenogoyazite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 3.33 |
| Attakolite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 3.09 |
| Bario-olgite | 4.00 / 4.50 | 4.00 |
| Bario-orthojoaquinite | 5.00 / 5.50 | 3.96 |
| Bariopyrochlore | 4.50 / 5.00 | 4.00 |
| Barytolamprophyllite | 2.00 / 3.00 | 3.62 |
| Bassoite | 4.00 / 4.50 | 2.94 |
| Batiferrite | 6.00 / 6.00 | |
| Bellbergite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.20 |
| Belovite-(Ce) | 5.00 / 5.00 | 4.19 |
| Belovite-(La) | 5.00 / 5.00 | 4.19 |
| Benauite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 3.65 |
| Benstonite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 3.60 |
| Bjarebyite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 4.02 |
| Bobtraillite | 5.50 / 5.50 | 3.16 |
| Brewsterite-Ba | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.45 |
| Brewsterite-Sr | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.45 |
| Burbankite | 3.50 / 3.50 | 3.50 |
| Burovaite-Ca | 2.73 | |
| Bussenite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 3.63 |
| Bykovaite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 2.98 |
| Bøggildite | 4.00 / 5.00 | 3.66 |
| Bøgvadite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 3.85 |
| Cairncrossite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 2.85 |
| Calcioancylite-(Ce) | 4.00 / 4.50 | |
| Calcioburbankite | 3.00 / 4.00 | 3.45 |
| Calcjarlite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 3.51 |
| Carbocernaite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 3.53 |
| Carbokentbrooksite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 3.14 |
| Caryochroite | 2.50 / 2.50 | 2.99 |
| Celestine | 3.00 / 3.50 | 3.90 |
| Cerite-(La) | 5.00 / 5.00 | 4.70 |
| Chabazite-Ca | 4.00 / 4.00 | 2.05 |
| Chabazite-Na | 4.00 / 4.00 | 2.05 |
| Chabazite-Sr | 4.00 / 4.50 | 2.16 |
| Charoite | 5.00 / 6.00 | 2.54 |
| Chivruaiite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 2.40 |
| Cleusonite | 6.00 / 7.00 | 4.74 |
| Clinophosinaite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 2.85 |
| Clinoptilolite-K | 3.50 / 4.00 | 2.10 |
| Cordylite-(La) | 4.00 / 4.00 | 4.33 |
| Crawfordite | 3.00 / 3.00 | 3.05 |
| Crichtonite | 5.00 / 6.00 | 4.46 |
| Dachiardite-Ca | 4.00 / 4.50 | 2.14 |
| Daqingshanite-(Ce) | 5.00 / 5.00 | 3.81 |
| Deloneite | 5.00 / 5.00 | |
| Delrioite | 2.00 / 2.00 | 3.10 |
| Dessauite-(Y) | 6.50 / 7.00 | 4.68 |
| Dickinsonite-(KMnNa) | 3.50 / 4.00 | 3.42 |
| Direnzoite | 4.50 / 4.50 | 2.12 |
| Dissakisite-(La) | 6.50 / 7.00 | 3.79 |
| Diversilite-(Ce) | 5.00 / 5.00 | 3.68 |
| Donnayite-(Y) | 3.00 / 3.00 | 3.30 |
| Dualite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.84 |
| Epidote-(Sr) | ||
| Eveslogite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.85 |
| Ewaldite | 3.25 | |
| Faizievite | 4.00 / 4.50 | 2.82 |
| Feklichevite | 5.50 / 5.50 | 2.87 |
| Fengchengite | ||
| Ferrierite-Mg | 3.00 / 3.50 | 2.06 |
| Ferrierite-Na | 3.00 / 3.50 | 2.06 |
| Ferrokentbrooksite | 5.00 / 6.00 | 3.06 |
| Ferronordite-(Ce) | 5.00 / 5.50 | 3.46 |
| Ferronordite-(La) | 5.00 / 5.00 | 3.54 |
| Fersmanite | 5.50 / 5.50 | 3.44 |
| Fluorbritholite-(Ce) | 5.00 / 5.00 | 4.66 |
| Fluorcalciobritholite | 5.50 / 5.50 | 4.20 |
| Fluorcaphite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 3.60 |
| Fluorlamprophyllite | ||
| Fluorstrophite | 5.00 / 5.00 | |
| Fontarnauite | ||
| Footemineite | 4.50 / 4.50 | 2.87 |
| Georgbarsanovite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 3.05 |
| Gjerdingenite-Ca | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.79 |
| Gmelinite-Ca | 4.50 / 4.50 | 2.03 |
| Goedkenite | 5.00 / 5.00 | 3.83 |
| Goyazite | 4.00 / 5.00 | 3.16 |
| Gramaccioliite-(Y) | 6.00 / 6.00 | 4.66 |
| Grandaite | 4.38 | |
| Graulichite-(Ce) | 3.90 | |
| Gutkovaite-Mn | 5.00 / 5.00 | 2.83 |
| Haradaite | 4.50 / 4.50 | 3.80 |
| Hennomartinite | 4.00 / 4.00 | 3.00 |
| Heulandite-Ba | 3.50 / 3.50 | 2.35 |
| Heulandite-Ca | 3.00 / 3.50 | 2.20 |
| Heulandite-K | 3.00 / 3.50 | 2.20 |
 mineraly.fr
mineraly.fr
 mineraly.co.uk
mineraly.co.uk
 mineraly.com.de
mineraly.com.de
 mineraly.it
mineraly.it
 mineraly.es
mineraly.es
 mineraly.nl
mineraly.nl
 mineraly.pt
mineraly.pt
 mineraly.se
mineraly.se